Understanding human-level performance
Human-level error gives an estimate of Bayes error.
Example 1: Medical image classification This is an example of a medical image classification in which the input is a radiology image and the output is a diagnosis classification decision.
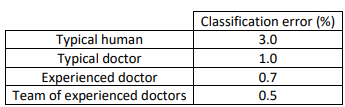
The definition of human-level error depends on the purpose of the analysis, in this case, by definition the Bayes error is lower or equal to 0.5%.
Example 2: Error analysis
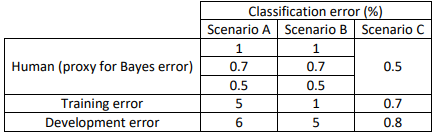
Scenario A In this case, the choice of human-level performance doesn’t have an impact. The avoidable bias is between 4%-4.5% and the variance is 1%. Therefore, the focus should be on bias reduction technique.
Scenario B In this case, the choice of human-level performance doesn’t have an impact. The avoidable bias is between 0%-0.5% and the variance is 4%. Therefore, the focus should be on variance reduction technique.
Scenario C In this case, the estimate for Bayes error has to be 0.5% since you can’t go lower than the human-level performance otherwise the training set is overfitting. Also, the avoidable bias is 0.2% and the variance is 0.1%. Therefore, the focus should be on bias reduction technique.
Summary of bias/variance with human-level performance
Human - level error – proxy for Bayes error If the difference between human-level error and the training error is bigger than the difference between the training error and the development error. The focus should be on bias reduction technique
If the difference between training error and the development error is bigger than the difference between the human-level error and the training error. The focus should be on variance reduction technique