-
Chapter 9: CONCEPT OF BUDGETING
Introduction
The
financial year of India runs from 1 April to 31 march. The
budget or Annual Financial Statement should separate revenue
expenditure from the rest. Therefore the budget comprises of
revenue budget and capital budget.
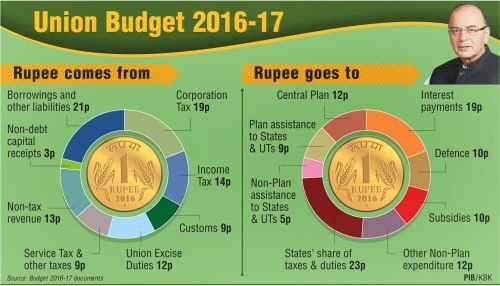
Fig 1: Budget 2016 theme – “Transform India”.
Revenue account:
This shows the current receipts of the government and the expense that can be met from these.
Revenue receipts:
1. Tax revenues – taxes and duties.
2. Non tax revenues – interest on loans, grants in aid from foreign bodies, payment for services, dividends from investment.
Taxes are direct taxes like
income tax, corporation, estate duty, wealth tax [abolished],
and security transaction tax. All these are imposed directly on
individuals.
Indirect taxes are excise duty,
customs duty, service tax that is paid by consumers indirectly
to the government. India
follows a progressive taxation regime on income of
individuals which means higher the income higher the tax.
But for corporate its charges a proportional
tax which is a fixed proportion of its profit.
Revenue expenditure:
It is all the expenditure incurred by the government which doesn’t result in physical or financial asset creation.
E.g.: interest on borrowing, subsidies, pensions, salaries, grants to other entities.
The budget may classify revenue expenditure into plan and non plan. Plan expenditure is incurred on central five year plans and state and UT five year plans. Non plan component is more that the plan component and includes interest payment, defense, salaries, subsidies and pensions.
Capital accounts:
This is an account of assets and liabilities of the central government that takes into account change in capital. This shows capital requirements of the government and their pattern of financing.
Capital receipts:
1. Loans raised by government from public, banks, RBI, selling of treasury bonds, foreign entities via external commercial borrowings.
2. Money received by selling shares of P.S.U.
3. Recoveries of loans given by central government
4. Small savings, post office credit, provident fund.
Capital expenditure:
1. Loans to states and UT’s.
2. Expenditure on acquisition of land, machinery, building, shares.
Capital budget also has plan and non plan components. Plan component means the expenditure is on five year plan of centre and states. Non plan component means the expenditure is on general, social, economic services of the government.
Fiscal responsibility and budget management act, 2003 mandates that along with the budget the following documents should also be presented:
1. Medium term fiscal policy statement
2. Fiscal policy strategy statement
3.
Macroeconomic
framework
statement
Indicators of government deficit:
1. Revenue deficit: refers to the revenue expenditure being in excess of revenue deficit.
Revenue deficit = revenue expenditure – revenue income
2. Fiscal deficit: difference between the government’s total expenditure and its total receipts including borrowing.
Gross fiscal deficit = net borrowing from home + borrowing from RBI + borrowing from abroad.
3. Primary deficit: gross fiscal deficit – net interest payments.
Budget 2017-18
Key features :
Plan and non plan distinction to be removed
Railway budget and general budget to be merged.
Post demonetization strategy to boost spending to be unveiled.
GST shall be implemented.
The railway budget has been of a size less than the defence budget and so a need to separate presentation was not felt. The merger of budget shall ensure freedom from payment of dividend to the government. This can be utilized by railways for capital investment.
Plan expenditure was the expense of creating productive assets and non plan was on routine expenses like salaries, pensions, subsidies. This shall be replaced by a better indicator of productivity like capital and revenue expenditure.
Advancing the budget date shall ensure that the ministries have funds to spend right from the start of the fiscal year.
Vote on Account v/s Interim Budget
| Vote on Account | Interim Budget |
|---|---|
| This budget accounts for only the expenditure part and cannot have tax proposals. | This budget is like a routine budget and can have taxation as well as expenditure proposals. |
| Passed by only the Lok Sabha | Passed by both houses but Rajya Sabha can only stall it for 14 days. However Rajya Sabha can discuss it and reject it but such recommendations or rejections are non binding on the Lok Sabha. |
| It is a temporary arrangement made as the Annual Budget passing is a two month long exercise and till that time the finance needed to run the government and the country has to be arranged. So for two months money is allocated by the Vote on Account. This amount is [ Total Amount of Budget / 6 ] as full budget is for 12 months and Vote on Account is for 2 months so 1/6th of the period. | It allocated money for full year. But by convention it is presented during the election year when the Government might change and so no major reforms or proposals are introduced. After election the new government can have a new full scale budget. |
Solved Question Papers
Q.Consider the following statements:
1. National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) helps in promoting the financial inclusion in the country.
2. NPCI has launched RuPay, a card payment scheme.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (UPSC CSAT 2017)
1 only
2 only
Both 1 and 2
Neither 1 nor 2
Ans . C
NPCi is a not-for-profit company formed by various banks, with primary objective of providing cost-effective payment solutions to the banksNPCi’s solutions such as IMPS, BHIM, RuPay, AEPS etc. have indeed helped in financial inclusion
NPCi launched Rupay card in 2012, as 7th payment gateway in the world
Q.Which of the following is a most likely consequence of implementing the ‘Unified Payments Interface (UPI)’? (UPSC CSAT 2017)
Mobile wallets will not be necessary for online payments.
Digital currency will totally replace the physical currency in about two decades
FDI inflows will drastically increase.
Direct transfer of subsidies to poor people will become very effective.
Ans . A
Mobile wallets will not be necessary, because your mobile number is directly linked with the bank account
Q.Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)?
1. It decides the RBI’s benchmark interest rates.
2. It is a 12-member body including the Governor of RBI and is reconstituted every year.
3. It functions under the chairmanship of the Union Finance Minister.
Select the correct answer using the code given below : (UPSC CSAT 2017)
1 only
1 and 2 only
3 only
2 and 3 only
Ans . A
MPC has 6 members, not 12; and it’s headed by RBI governor and not Finance Minister
Q. Which of the following statements best describes the term ‘Scheme for Sustainable Structuring of Stressed Assets (S4A)’, recently seen in the news?(UPSC CSAT 2017)
It is a procedure for considering ecological costs of developmental schemes formulated by the Government.
It is a scheme of RBI for reworking the financial structure of big corporate entities facing genuine difficulties.
It is a disinvestment plan of the Government regarding Central Public Sector Undertakings
It is an important provision in ‘The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code’ recently implemented by the Government.
Ans . B
S4A is RBI’s scheme for restructuring of corporate loans
Q.What is the purpose of setting up of Small Finance Banks (SFBs) in India?
1. To supply credit to small business units
2. To supply credit to small and marginal farmers
3. To encourage young entrepreneurs to set up business particularly in rural areas.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:(UPSC CSAT 2017)
1 and 2 only
2 and 3 only
1 and 3 only
1, 2 and 3
Ans . A
Third is an indirect benefit not direct
Q.Who among the following can join the National Pension System (NPS)? (UPSC CSAT 2017)
Resident Indian citizens only
Persons of age from 21 to 55 only
all State Government employees joining the services after the date of notification by the respective State Governments
All Central Government employees including those of Armed Forces joining the services on or after 1st April, 2004
Ans . C
NPS was compulsory for new central govt recruits (except armed forces) WEF 1/1/2004, Any Indian between 18 to 55 can join NPS , NRI open NPS account
Q.What is/are the most likely advantages of implementing ‘Goods and Services Tax (GST)’?
1. It will replace multiple taxes collected by multiple authorities and will thus create a single market in India.
2. It will drastically reduce the ‘Current Account Deficit’ of India and will enable it to increase its foreign exchange reserves.
3. It will enormously increase the growth and size of economy of India and will enable it to overtake China in the near future.
Select the correct answer using the code given below: (UPSC CSAT 2017)
1 only
2 and 3 only
1 and 3 only
1, 2 and 3
Ans . A
Exports will become ZERO RATED under GST, GST is unlikely to ‘drastically’ reduce CAD , GST is unlikely to enormously increase size of our economy
Q.With reference to the ‘Prohibition of Benami Property Transactions Act, 1988 (PBPT Act)’, consider the following statements:
1. A property transaction is not treated as a benami transaction if the owner of the property is not aware of the transaction.
2. Properties held benami are liable for confiscation by the Government.
3. The Act provides for three authorities for investigations but does not provide for any appellate mechanism.
Which of the statements .given above is/are correct? (UPSC CSAT 2017)
1 only
2 only
1 and 3 only
2 and 3 only
Ans . B
an appellate tribunal, and they’re required to finish case within one year
Q.Consider the following statements :
1. Tax revenue as a percent of GDP of India has steadily increased in the last decade.
2. Fiscal deficit as a percent of GDP of India has steadily increased in the last decade.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct ? (UPSC CSAT 2017)
1 only
2 only
Both 1 and 2
Neither 1 nor 2
Ans . D
Q.The terms ‘Marginal Standing Facility Rate’ and ‘Net Demand and Time Liabilities’, sometimes appearing in news, are used in relation to (UPSC CSAT 2014)
banking operations
communication networking
military strategies
supply and demand of agricultural products
Ans . A
Q.What is/are the facility/facilities the beneficiaries can get from the services of Business Correspondent (Bank Saathi) in branchless areas?
It enables the beneficiaries to draw their subsidies and social security benefits in their villages.
It enables the beneficiaries in the rural areas to make deposits and withdrawals.
Select the correct answer using the code given below. (UPSC CSAT 2014)
1 only
2 only
Both 1 and 2
Neither 1 nor 2
Ans . C
Besides giving access to banking, it also enables government subsidies and social security benefits to be directly credited to the accounts of the beneficiaries, enabling them to draw the money from the bank saathi or business correspondents in their village itself.
Q.In the context of Indian economy; which of the following is/are the purpose/purposes of ‘Statutory Reserve Requirements’?
To enable the Central Bank to control the amount of advances the banks can create
To make the people’s deposits with banks safe and liquid
To prevent the commercial banks from making excessive profits
To force the banks to have sufficient vault cash to meet their day-to-day requirements
Select the correct answer using the code given below. (UPSC CSAT 2014)
1 only
1 and 2 only
2 and 3 only
1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans . B
RBI requires commercial banks to keep reserves in order to ensure that banks have a safe cushion of assets to draw on when account holders want to be paid.”
Q.If the interest rate is decreased in an economy, it will (UPSC CSAT 2014)
decrease the consumption expenditure in the economy
increase the tax collection of the Government
increase the investment expenditure in the economy
increase the total savings in the economy
Ans . C
The relationship between interest rate and investment Expenditure is illustrated by the investment curve of the economy.
The curve has downward slope, indicating that a drop in interest rate, causes the investment-spending to rise.
Q.There has been a persistent deficit budget year after year. Which of the following actions can be taken by the government to reduce the deficit?
1. Reducing revenue expenditure
2. Introducing new welfare schemes
3. Rationalizing subsidies
4. Expanding industries
Select the correct answer using the code given below. (UPSC CSAT 2015)
1 and 3 only
2 and 3 only
1 only
1,2,3 and 4
Ans . A
Introducing new welfare scheme will further inflate the budget. Expanding industries by budgetary support will not add anything in the short-run to the tax revenues of the government, and thus will increase the budget deficit.
Rationalizing subsidies and reducing revenue expenditure are two direct ways of reducing the fiscal burden of the government of India.