-
Chapter 3: URBAN INFRASTRUCTURE
Introduction
Statutory towns are those with urban local bodies and census towns are those with population more than 5000, density 400 persons / sq km and 75% male population involved in non agro work. There are more statutory towns than census towns in India.
Census classification of towns:
- Metro : 10 lakh+
- Tier 1: 1 lakh
- Tier 2; 50000 - 99999
- Tier 3: 20000 - 49999
- Tier 4: 10000 - 19999
- Tier 5: 5000 - 9999
- Tier 6: Less than 5000
Schemes for Urban Infrastructure
Sardar Urban HousingDiscontinuation of Rajiv Awaas Yojana [slum rehabilitation in urban areas] and Rajiv Rinn Yojana - meant for interest subsidy for EWS / LIG. Ministry of Housing and urban poverty alleviation to implement this by PPP, interest subvention and tax benefits on home loans.
Draft Model Tenancy Law
Rent control Act not amended to keep vote bank happy, the rent ceilings are very low and hence sub letting is done at high rates and landlords are at a loss. Eviction of tenants is tough giving the landlords little interest in maintaining homes which lead to building collapse.
Salient points:
- Earlier tenant refuses to pay higher rent then he cant be evicted without court case but now automatic eviction if tenant refuses to pay but a three month notice has to be given.
- Old act didn't apply to contracts less than 12 months so deliberate 11 months contract framed but now new Act shall apply to all rental contracts irrespective of period.
- Owner has to refund security deposit within 1 month of contract expiry.
- All rent agreement to be registered with state authority.
- landlord can enter house only from 7 am to 8 pm and after giving 24 hour notice.
Real Estate Development Bill
- Appoint state real estate authority and appellate tribunals.
- Builder has to register project with the authority before selling.
- Penalty for misselling, fine for missing deadline, change of structural plan needs approval of 2/3rd buyers.
RERA [Real Estate regulation and Development Act] specifies that all residential and commercial projects be covered under it. Due to legislation, a transparency in functioning of developers shall be created. The focus is also on grievance redressal in a cost effective and speedy manner. The capacity of this sector to attract investment from domestic and foreign sources shall increase. The Act also has capacity to boost confidence of home buyers and investors.
GST too has capcity to affect this segment as a low tax rate can bring down costs. GST has subsumed a large number of taxes at State, national and local level. However this sector depends on other ancillary industries like Steel, cement and so the effect of GST on these too is important.
Real Estate Investment Trusts are also an example of how investment can be brought into this sector. This will increase transparency and allow people to gain returns better than gold or other instruments. This will impact Current Account Deficit [CAD] as imports of gold might decrease.
Implications of Demonitization on Real estate sector
Real estate sector is the second largest employer of illiterate and unskilled workers after agriculture. It has backward linkages to 255+ different industries. Yet it has remained highly unorganised with large amount in cash transactions and poor corporate governance practices.
Implications of demonitization
- The secondary market in real estate sector i.e. where the properties are sold and purchased from the first buyers and not the developers, has seen high amount of black money. The impact of demonitization on this sector has led to reduction in business of brokers and sellers atleast for time being.
- Due to lack of cash unskilled workers are not being paid.
- Slowdown in the economy means new projects are delayed.
- Due to demonitization the properties might get cheaper in the short run. Speculative investors might not get returns as they expected so decline in their investment.
- Lending by banks to home buyers will increase as they have become flush with liquidity.
Additional steps needed:
- Implementation of real estate regulation act
- Move towards cashless property transactions and incentive cashless transactions reduction in stamp duty
- Speedier approvals to permissions and deemed clearance if approvals not given within deadline.
- Self certification to be made the norm with stringent punishment for flase declarations by builders.
- RERA focuses on only primary markets i.e. developers to buyers but not secondary markets i.e. brokers to buyers or buyers to other buyers. This sector needs to regulated by introduction of compulsory registration.
SMART CITIES
They offer quality of life, employment and investment opportunities with environment and social sustainability.
Fig 1: SMART city
Pillars of SMART CITY MISSION
Electricity:
- Digitally managed street lights, 10% of energy requirements met through renewable sources.
- Self healing against power outages, resilient against cyber attacks.
Water and Sanitation:
- Solid waste management. Segregation of waste at households, penalty for misuse of water, electricity.
- Rainwater harvesting, storm water drainage.
Transport
- Public transport - Bus, BRTS, Metro and monorail.
- Roads - Ring roads, bypass, underpass; move men not vehicles by supporting non motor vehicles - waterways, cycling, walking.
- 20% of houses for EWS / LIG
- 95% houses have schools, shopping, parks with 400m all integrated with ICT.
Education infrastructure
- Schools like pre primary, primary, secondary, senior secondary, colleges, technical education centers, professional courses to be setup.
- Golf courses, swimming pools and sports complex setup.
- Availability of tele - medicine, nursing homes, child care centers, maternity homes, medium to large hospitals, vet care centers to be setup on basis of population.
Civic Utilities
- 24*7 availability of water, electricity, emergency, fire and medical service.
- Telephones and WiFi to all.
Economic infrastructure
- Banking, ATM, financial services present.
- Skill development centers, incubation centers, export parks, financial centers, warehousing and freight terminals.
Finance of SMART city
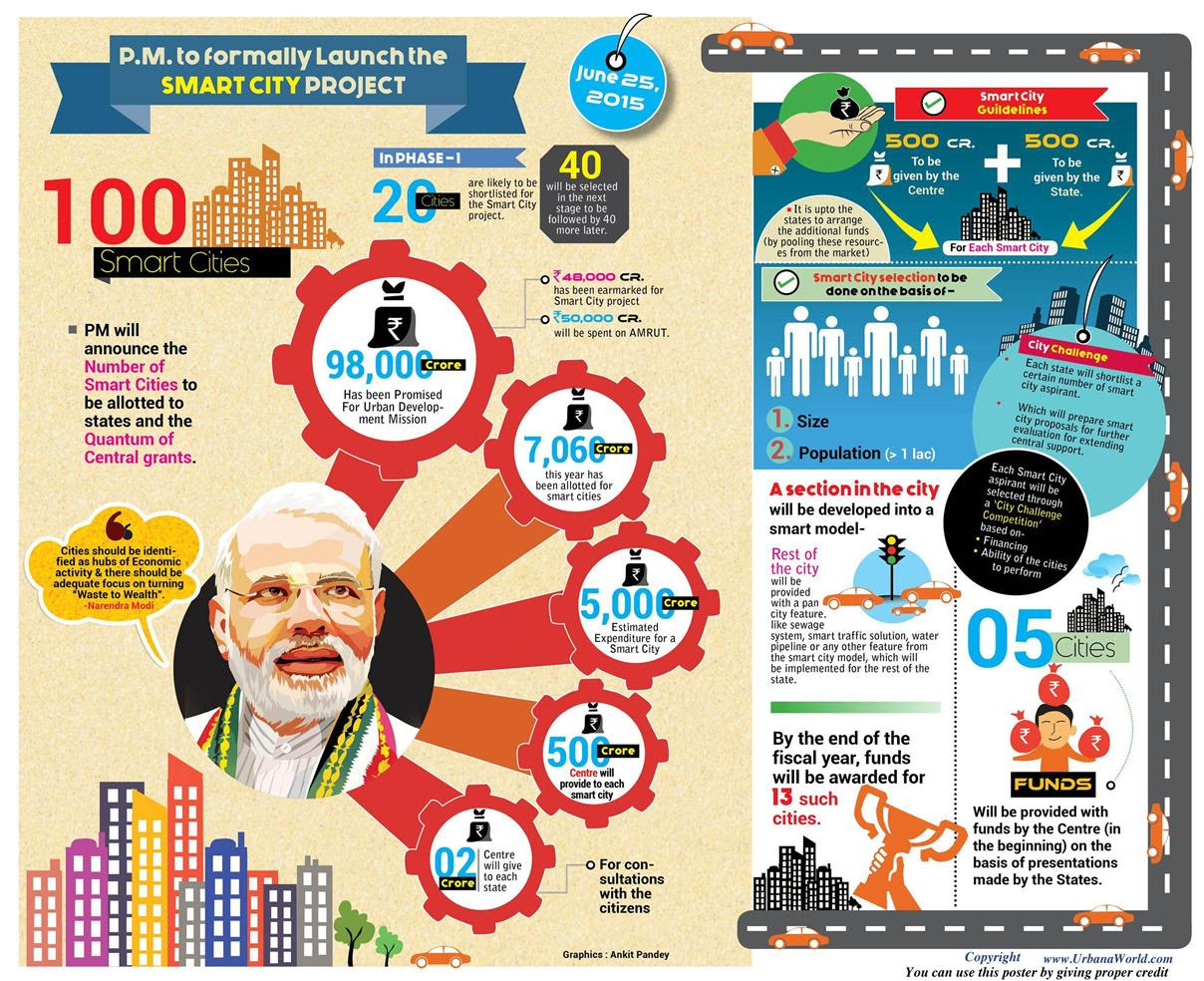
- 46000 crore for 100 smart cities one in each state.
- 60% of funds to infrastructure and 10% to e-governance and 10% performance based funding.
- 100% FDI allowed. 20000 sq m minimum area and $5 million minimum investment. lock in period of 3 yrs but if 30% houses for LIG then all conditions exempt.
Doing Business in India = 2017
‘Ease of doing business’ refers to the regulatory environment in a country to set up and operate a business. Every year, the World Bank compares the business environment in 190 countries in its Ease of Doing Business Report.
What parameters is a country ranked on?
In India, these rankings are based on the business environment in Mumbai and Delhi.
Note that these parameters are regulated by different agencies across the three tiers of government (i.e. central, state and municipal). For example, for starting a business, registration and other clearances are granted by central ministries such as Finance and Corporate Affairs. Electricity and water connections for a business are granted by the state electricity and water boards. The municipal corporations grant building permits and various other no objection certificates to businesses.
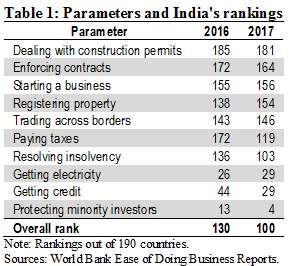
What has led to an improvement in India’s ease of doing business rankings?
Starting a business: India merged the application procedure for getting a Permanent Account Number (PAN) and the Tax Account Number (TAN) for new businesses. It also improved the online application system for getting a PAN and a TAN.
Getting credit and resolving insolvency: The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code passed in 2016 provides for a 180-day time-bound process to resolve insolvency. It also provides for the continuation of a debtor’s business during these proceedings. The Code allows secured creditors to opt out of resolution proceedings, and specifies that a debtor will be immune against creditor claims during the 180-day insolvency resolution process. Prior to the passage of the Code, it took 4.3 years in India to liquidate a business.
Paying taxes: The report notes that India made paying taxes easier by requiring that payments to the Employees Provident Fund are made electronically. Further, it introduced measures to ease compliance with corporate income tax.
Trading across borders: Import border compliance at the Jawaharlal Nehru Port, Mumbai was reduced. Export and Import costs were also reduced through increasing use of electronic and mobile platforms, among others.
Enforcing contracts: The introduction of the National Judicial Data Grid has made it possible to generate case management reports on local courts.
What are some of the other recommendations to improve the business environment in India?
Starting a business: The Committee had suggested that the procedures and time period for registration of companies should be reduced. In addition, a unique business ID should be created to integrate all information related to a debtor. This ID should be used as sole reference for the business.
Acquiring land, registering property: Under the current legal framework there are delays in acquiring land and getting necessary permissions to use it. These delays are on account of multiple reasons including the availability of suitable land and disputes related to land titles. It has been noted that land titles in India are unclear due to various reasons including legacy of the zamindari system, gaps in the legal framework and poor administration of land records.
The Standing Committee observed that the process of updating and digitising land records has been going on for three decades. It recommended that this process should be completed at the earliest. It also suggested that land ownership may be ascertained by integrating space technology and identification documents such as Aadhaar.
The Committee also recommended creating a single window for registration of property, to reduce delays.
Construction permits: In India, obtaining construction permits involves multiple procedures and is time consuming. The Standing Committee had observed that it took 33 procedures (such as getting no objection certificates from individual departments) over 192 days to obtain a construction permit in India. On the other hand, obtaining a similar permit in Singapore involved 10 procedures and took 26 days.
Taxation: Policy uncertainty and tax disputes have made foreign companies hesitant to do business in India. For ‘Make in India’ to succeed, there is a need for a fair, judicious and stable tax administration in the country. Further, it suggested that to reduce harassment of tax payers, an electronic tax administration system should be created. Such a system would reduce human interface during dispute resolution. Note that the Goods and Services Tax (GST) was introduced across the country from July 1, 2017. The GST framework allows for electronic filling of tax returns, among other measures.
Enforcing contracts: Enforcing contracts requires the involvement of the judicial system. The time taken to enforce contracts in India is long. For instance, the Standing Committee noted that it took close to four years in India for enforcing contracts. On the other hand, it took less than six months for contract enforcement in Singapore. This may be due to various reasons including complex litigation procedures, confusion related to jurisdiction of courts and high existing pendency of cases.
The Standing Committee recommended that an alternative dispute resolution mechanism and fast track courts should be set up to expedite disposal of contract enforcement cases. It suggested that efforts should be made to limit adjournments to exceptional circumstances only. It also recommended that certified practitioners should be created, to assist dispute resolution
Solved Question Papers
Q.Which one of the following is a purpose of `UDAY’, a scheme of the Government? (UPSC CSAT 2016)
Providing technical and financial assistance to start-up entrepreneurs in the field of renewable sources of energy
Providing electricity to every household in the country by 2018
Replacing the coal-based power plants with natural gas, nuclear, solar, wind and tidal power plants over a period of time
Providing for financial turnaround and revival of power distribution companies
Ans . D
Q.What is/are the purpose/purposes of `District Mineral Foundations’ in India?
1. Promoting mineral exploration activities in mineral-rich districts
2. Protecting the interests of the persons affected by mining operations
3. Authorizing State Governments to issue licences for mineral exploration
Select the correct answer using the code given below. (UPSC CSAT 2016)
1 and 2 only
2 only
1 and 3 only
1, 2 and 3
Ans . B
Q.`SWAYAM’, an initiative of the Government of India, aims at (UPSC CSAT 2016)
promoting the Self Help Groups in rural areas
providing financial and technical assistance to young start-up entrepreneurs
promoting the education and health of adolescent girls
providing affordable and quality education to the citizens for free
Ans . D
Quiz
Score more than 80% marks and move ahead else stay back and read again!