-
Chapter 3: COMMERCE
Introduction
Department of Commerce aims to create an enabling environment and infrastructure for growth of exports. Foreign Trade Policy 2015 - 2020 was formulated and implemented by it.
India was the founding member of WTO in 1995. It also was the first country to allow duty free quota free access to its markets to the least developed countries.
Indian Trade
Indian trade increased to 40% of the GDP with exports becoming 16% of the GDP. Export of goods and services account for 25% of the GDP.The top exports of India are Petroleum products, gems, textiles, , chemicals and agri products.
The top imports are petroleum, gems, chemicals, electronics and machinery.
India is the 19th largest exporter with 1.7% of World exports and 12th largest importer with 2.4% of world imports. China is the top exporter and USA is the top importer of the World.
Indian service exports are 3.2% of the World making it the 8th largest. Imports of services are 10th largest in the world [2.6%]. USA is the top importer and exporter of services in the World.
Trade Scenario
The Indian exports were mainly in Asia with 49% of the total going there. North and south america were 19% followed by Europe 18% [ EU countries - 15%]. USA [13.7%], UAE [10%], Hong kong, China and Saudi Arabia being next.
59% of Indian imports were from Asia, Europe 16% and American continent 13%. In individual countries China had a share of 13.5% followed by Saudi Arabia 6.2%, UAE, Switzerland and USA.
Guar gum is the largest export of the farm sector.Government Schemes of FTP -2015
All export related schemes of various sectors and services are now clubbed as single scheme for merchandise and service.
Merchandise Exports from India Scheme
- Most of agri commodities are covered for all global markets and other commodities are covered for markets of developed and emerging countries only.
- When such notified goods are exported to notified markets duty scrips are issued to exporter which can be used to make payments of customs duty, service tax or excise duty.
- A scrip is a chit which is of a value equal to certain percent of the exported consignment [FOB- Free on board]. This is used for payment of import duties or taxes on imported inputs.This is transferable i.e. can be sold in market.
- Status holders are exporters who can get various benefits like self declaration at ports and minimal documentation.
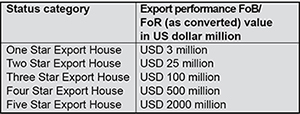
- All service providers exporting services from India shall get transferable duty credit scrips with value 3-5% of the net foreign exchange earned.
Types of Trade Agreements
- Preferential trade agreements: liberate tariff on limited products. Oldest one was in 1976 with Asian - Pacific countries [Bangladesh, India, China, Sri lanka, South Korea]
- Free trade agreements: eliminate tariff on items of trading partners. [ Latest was in 2015 with ASEAN countries]
- Comprehensive Economic cooperation agreement / Comprehensive economic partnership agreement / Broad based trade and investment agreement: covers goods, services, IPR, mutual recognition etc.
Doha Round of WTO:
The deadlock to ministerial talks of WTO has been existing since 2001 but finally in Bali round [Ninth ministerial round] a break through was achieved.
Decisions that impact India were:
- Public stock holding to food security
- Agreement on trade facilitation
The Public stockholding norms which were decided would have put India's Food security mission in threat. However due to negotiations it was decided that till 2017 no country can challenge the food security stock holding limits of developing countries. Later due to India's insistence this moratorium period was extended till a suitable solution could be found.
This enabled India to agree on the Trade Facilitation Agreement.
Trade Disputes
Dept of Commerce defends Indian interests at the dispute settlement of WTO.
- USA had challenged the Indian government decision to ban imports of poultry products from countries having an outbreak of Avian flu. However India lost this case as it couldn't prove that the ban was based on scientific evidence.
- US had imposed high counterveiling duty on Indian carbon steel products. This was challenged and India won this case.
- US had challenged the domestic sourcing requirement in Solar products made in India for the National solar mission. The result is expected on this.
Special Economic Zones
Asia's first SEZ was in Kandla in 1965.Currently 202 SEZ's are exporting with 114 are IT SEZ's and remaining are multi product or sector specific. The total units in them are 4100.
EPZ that existed before the SEZ Act of 2005 were converted to SEZ's.
Aim of SEZ:
- Promote domestic and foreign investment
- Develop quality infrastructure
- Increase job creation
- Increase exports of goods and services.
- Generate additional economic activity.
Shipping and Port related improvements
The government is considering increasing the share of Direct Port Delivery of containers to the pre approved clients instead of waiting at the Ports for customs clearance. The cost of keeping the containers at the ports for the day is Rs. 10000 this includes logistics, inventory and transaction cost. Thus DPD will facilitate cost savings and promote ease of doing business.
Other improvements were converting the ports that operated based on paper records to electronic data interchange.
All ports have been asked to integrate the Port Community System and Terminal Operators Filling System with ICEGATE - E-Commerce Portal of Central Board of Excise and Customs.
Official YouTube Channel of UPSCFEVER - #1
Quiz
Score more than 80% marks and move ahead else stay back and read again!