UGC NET - Dec 2012
Ans .
B
- Explanation :
THE DIGITAL ECOSYSTEM OF A BUSINESS IS THE COMBINATION OF ALL RELEVANT DIGITAL TOUCHPOINTS, THE PEOPLE THAT INTERACT WITH THEM, AND THE BUSINESS PROCESSES AND TECHNOLOGY ENVIRONMENT THAT SUPPORT BOTH.Thus it can be said that Eco system is a Frame work for building Internet Market
Ans .
B
- Explanation :
Efficiency E can never be more than 1 or 100% even 1 is just theortical
Speed up for multiprocessor Sp can never exceed (P) no of processors
hence E≤1 and Sp≤p. Hence,The efficiency (E) and speed up (S) for Multiprocessor with p processors satisfies : E ≤ 1 and Sp ≤ p
Ans .
B
- Explanation :
List-I List-II
a. Critical region 2. Mutual exclusion
b. Wait/signal 1. Hoares Monitor
c. Working set 3. Principal of locality
d. Dead lock 4. Circular wait
Ans .
B
- Explanation :
Piggybacking of acknowledments:The ACK for the last received packet need not be sent as a new packet, but gets a free ride on the next outgoing data frame(using the ACK field in the frame header). The technique is temporarily delaying outgoing ACKs so that they can be hooked on the next outgoing data frame is known as piggybacking. But ACK can't be delayed for a long time if receiver(of the packet to be acknowledged) does not have any data to send.
Ans .
C
- Explanation :
It is the computational process of discovering patterns in large data sets involving methods at the intersection of artificial intelligence, machine learning, statistics, and database systems..Data Mining is process of extracting previously non known valid and actionable information from large data to make crucial business and strategic decisions.
Ans .
A
- Explanation :
The aspect ratio of an image describes the proportional relationship between its width and its height. It is commonly expressed as two numbers separated by a colon, as in 16:9..The aspect ratio of an image is defined as : the ratio of width to its height measured in unit length.
(a) More than one program may be loaded into main memory at the same time.
(b) If a program waits for certain event another program is immediately scheduled.
(c) If the execution of a program terminates, another program is immediately scheduled.
Ans .
D
- Explanation :
More than one program loaded into main memory at the same time. If a program waits for certain event another program is immediately scheduled If the execution of a program terminates, another program is immediately scheduled In a multi-programming system there are one or more programs loaded in main memory which are ready to execute. Only one program at a time is able to get the CPU for executing its instructions (i.e., there is at most one process running on the system) while all the others are waiting their turn. The main idea of multi-programming is to maximize the use of CPU time. Indeed, suppose the currently running process is performing an I/O task (which, by definition, does not need the CPU to be accomplished). Then, the OS may interrupt that process and give the control to one of the other in-main-memory programs that are ready to execute (i.e. process context switching). In this way, no CPU time is wasted by the system waiting for the I/O task to be completed, and a running process keeps executing until either it voluntarily releases the CPU or when it blocks for an I/O operation. Therefore, the ultimate goal of multi-programming is to keep the CPU busy as long as there are processes ready to execute.
Ans .
D
- Explanation :
Given p=3,q=11. n=(p X q) = (3 X 11)=33
m=(p-1)X(q-1) = (2 X 10)=20
Find a small odd integer e, that is relatively prime to m.
If e=3, then GCD(3,20)=1. e should be small and prime and so we let e=3.
d is given, d=7.
Public key = (e,n). (Values of e and n are known).
To encrypt a message, we apply the public key to the function
E(s) = se(mod n)
where s is the given message and e and n represent the public key integer pair. In the above question, the plain text M = 5. Plain text needs to be encrypted using the above formula.
=53(mod 33)
= 125 (mod 33)
= 26
As a result, the encrypted message E(s) = 26. This is what gets transmitted.
Ans .
D
- Explanation :
OR can be solved using single layer perception and XOR problem can be solved using radial basis function.An OR problem and a XOR problem to solve. Then,OR problem can be solved using single layer perception and XOR problem can be solved using radial basis function.
Ans .
C
- Explanation :HTTP is a Transport layer protocol,TCP is an Application layer protocol,BGP ia a Network layer protocol and HDLC is Data Link Layer protocol
Ans .
A
- Explanation :The time complexities of - Bellman Ford algorithm = O(mn),Kruskals algorithm = O (m log n),Floyd Warshall algorithm = O (n3) and Topological sorting = O(n + m)
Ans .
D
- Explanation :
If V1 = 2I – J + K and V2 = I + J – K, then the angle between V1 & V2 and a vector perpendicular to both V1 & V2 shall be: 90০ and (–2I – J + 3K)
Ans .
C
- Explanation :
putting value of X from 0 to 10 in membership function =x/x+2 we get
0/2 , 1/3 , 2/4 ,3/5 ,4/6 ,5/7 , 6 /8 , 7/9 , 8/10 , 9/11 , 10/12 means they are belonging with degree 0,0.33,0.5,0.6 .........0.83
here alpha cut =0.5 so first two elements will not be included in the result as their degree of belongingness <0.5
so ans will be C
Ans .
D
- Explanation :
By applying master theorem, we can get the answer
Ans .
A
- Explanation :
0 - 126 = Class A
128 - 191 = Class B
192 - 223 = Class C
224 - 255 = Class D
So ans is A.
Here,
Ans .
B
- Explanation :
ans is B both are complex numbers.The Mandelbrot set is the set of complex numbers c for which the function does not diverge when iterated fromz=0,
Here,
Ans .
A
- Explanation :
Hence Ans is A
Ans .
C
- Explanation :
Total number of basic solutions are given by the eqn n!/m! * (n-m)! , where m=3 no of basic variables and n=3+2 =5 total no of variables. hence total soln =5!/3!2!=5x4/2=10. Ans is C
Ans .
C
- Explanation :
Ans .
C
- Explanation :
The number of ways to distribute n distinguishable objects into k distinct boxes so that ni objects are placed in box i, i=1, ..., k, and n1+...+nk = n, is n1 !/ n1 .n2. n3.....nk
Ans .
D
- Explanation :
It can be reduced as 11 similar balls into 3 different boxes...
x>=1 , x2>=2, x3>=3
So 11 -(1+2+3) = 5 (remaining balls)
It is combination with repetition...
With 5 similar items and 3 different items...
So ans is (5+3-1)C5
That is 7C5
Ans .
C
- Explanation :
Calinsock Active-X Control provides an interface to the TCP/IP suit protocols in Windows95 and Windows NT
Ans .
B
- Explanation :
T flip flop toggles the state if input T is 1, and does not change state if input T is 0. T flip flop is a clocked (synchronous or edge-triggered) flip flop. Edge triggered flip flops can only change its values at the edge of a clock, in absence of edge does not change its state, remains same. In given circuit, clock symbol is showing that it is positive edge triggering (low to high change). Note that there are mainly four different types of clock-triggering methods. Now, we need to find out Q0Q1 after 4 clock cycles.
Initial: 00 States Q0 and Q1 are zero
Clock 1: 11 State Q0 changed to 1 because input T is 1 and previous state was 0 and State Q1 changed to 1 because input T is 1 and previous state was 0.
Clock 2: 01 State Q0 changed to 0 because input T is 1 and previous state was 1 and State Q1 remains same because clk value is 0.
Clock 3: 10 State Q0 changed to 1 because input T is 1 and previous state was 0 and State Q1 changed to 0 because input T is 1 and previous state was 1.
Clock 4: 00 State Q0 changed to 0 because input T is 1 and previous state was 1 and State Q1 remains same because clk value is 0.
Ans .
B
- Explanation :
Few properties of Primal and dual
1)The dual of dual linear programming problem is again the primal problem
2)If either the primal or dual problem has unbounded soln the other problem(dual or primal) has no feasible soln
3))If either the primal or dual problem has a finite optimal soln the other one also possesses the same and the optimal value of the objective function of 2 problems are same
so by property 2 ans is A
note :unbounded soln means there is no limit i.e away from the origin
feasible soln :- if there is some common are between lines towards origin
Unfeasible soln : if there is no common shaded area between lines
for relationship between primal and dual
Ans .
C
- Explanation :
The number of distinct bracelets of five beads made up of red, blue, and green beads (two bracelets are indistinguishable if the rotation of one yield another) is,51
Ans .
C
- Explanation :
Mobile Applications can be classified as Private data, Public data, Shared data
Ans .
B
- Explanation :
Ans .
A
- Explanation :

Ans .
D
- Explanation :
connect First 4 Lamps(L1 , L2 , L3 , L4) to extension 1 and take power from Extension 2 . In Extension 2 we can connect only 3 lamps because out of 4 one port is busy to supply power to extension 1. Similarly, For other extensions we can connect only 3 lamps because one port is busy to supply power to other extension. Connect Last Extension (Ex 19) to Electric outlet.
a. Downlink control 1. 100 Mbps
b. Radio communication data rate 2. Residency latency (RL)
c. The average duration of user’s stay in cell 3. Sending data from a BS to MD
d. Residency latency (RL) 4. 2-Mbps
Ans .
B
- Explanation :
Downlink control -> Sending data from a BS to MD , Radio communication data rate -> 2-Mbps, The average duration of user’s stay in cell -> Residency latency (RL) and Residency latency (RL) -> 100 Mbps
Use of Downlink control in Mobile Computing Architecture : The base station subsystem (BSS) is the section of a traditional cellular telephone network which is responsible for handling traffic and signaling between a mobile Device and the network switching subsystem. So this statement indicates Downlink control is used to Sending data from a BS to MD.
Ans .
D
- Explanation :
No flag is set when ‘JMP’ instruction is executed
Ans .
B
- Explanation :
A thread is a light weight Process. We might call it that way because a thread, like a process, is a way to have a parallel, concurrent, flow of execution. But contrary to a process, a thread shares the same memory as the other threads in the same process, instead of having a completely separate memory.
Ans .
B
- Explanation :
In Z-buffer algorithm an arbitrary number of objects can be handled because each object is processed one at a time
Ans .
B
- Explanation :
A = {2,3,5,7} B= {2,5,8,9}
A∪B = {2,3,5,7,8,9}
Power set going to have 26 elements which is 64
Ans .
C
- Explanation :
Win main is the function which is provided to create windows application .The user-provided entry point for a graphical Windows-based application.
Ans .
B
- Explanation :
because in nested subroutine calls we used to push old subroutines into stack and pointing most recent call with stack pointer.
Ans .
A
- Explanation :
A system call, sometimes referred to as a kernel call, is a request by an active process made via a software interrupt for a service performed by the kernel. The system call interface is the basic interface between a program and the kernel
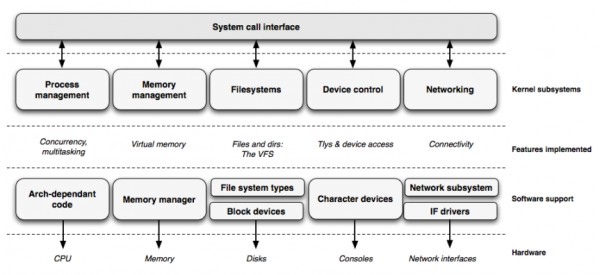
A kernel is the central part of an operating system. It manages the tasks of the computer and the hardware - most notably memory and CPU time. There are two types of kernels: A microkernel, which only contains basic functionality; A monolithic kernel, which contains many drivers.
Ans .
B
- Explanation :
The class of regular sets is not closed under inverse homomorphisms
Actually regular sets is closed under inverse homomorphisms.
Ans .
B
- Explanation :
When a programming Language has the capacity to produce new data type, it is called as, Extensible Language
Ans .
C
- Explanation :
Windows 2000 is an operating system for use on both client and server computers. It was produced by Microsoft and released to manufacturing on December 15, 1999[5] and launched to retail on February 17, 2000.[6] It is the successor toWindows NT 4.0, and is the last version of Microsoft Windows to display the "Windows NT" designation.[7] It is succeeded byWindows XP (released in October 2001) and Windows Server 2003 (released in April 2003). During development, Windows 2000 was known as Windows NT 5.0.