Section 4:Past Years' Solved Questions from the SNAP
1.SNAP 2011
Directions for Questions 1 and 2:
Each question consists of a set of numbered statements. Assume that each one of these statements is individually true. Each of the four choices consists of a subset of these statements. Choose the subset as your answer where the statements therein are logically consistent among themselves:- Explanation :
The first thing you should notice in this question, is that out of the given 8 statements in this question, only statements G and H are event based statements. All other statements specify conditions and are in the following formats: (i) If A then B-which means that if A occurs then B occurs; (ii) Whenever A then B (which essentially means the same thing as 'If A then B'); (iii) A only if B; which means that A can occur only if B occurs but A is not sure to occur if B occurs. (iv) Only if A then B-which means that A causes B and also that A is the only cause that leads to B. (v) If A then Not B-which means that if A happens B would not happen. (vi) Unless A, B-which means that B would happen unless A happens. Once you realize this you can move onto evaluate the options in the question. For instance option (a) gives us the combination C, D, F, G and H. Since G and H are events, we need to evaluate if G leads to H given that C, D and F are true. C states: If people are rewarded then they will not change their lifestyle. F states: Unless people change their lifestyle, temperature rises. D states: If the temperature rises, then the water level in the coastal areas rises. With these conditions if we know from G that people are rewarded, our thinking in order to check the logical consistency of the statements in this group would go as under: People are rewarded Æ Hence they would not change their lifestyle (From C)Æ Since, people do not change their lifestyle, the temperature would rise (from F) Æ If the temperature rises, the water level in the coastal areas rises (From D). But the cause effect relationship given between G and H is: People are rewarded Æ Water level in the coastal areas does not rise. This cause-effect relationship is opposite to what would happen if we consider the logic chain of C-F-D as shown above. Thus, the statements in option (a) are inconsistent among themselves. You will need to think of the logical consistency of the statements in options (b) and (c) similarly. The following checking structure would work for option (b). The statements in option (b) are: G, F, D, B and H. Amongst these, G and H are again the cause and effect statements as they are the only events amongst the statements given. Hence, the cause-effect relationship we need to test is: People are rewarded (leading to) Æ Water level in the coastal areas does not rise; under the conditions specified by the statements B, D, F. B states: People change their lifestyle only if they are rewarded. Note here that this means that in case people are rewarded, they may change their lifestyle but it is not sure whether they would change their lifestyle if they are rewarded. What is sure is that if they are not rewarded they would not change their lifestyle. It is similar to the statement we often hear: " You would succeed only if you work hard" does not mean that if you worked hard you would necessarily succeed. You may or may not succeed in case you work hard, but what is sure is that if you do not work hard, you would not succeed. F states: Unless people change their lifestyle, temperature rises. D states: If the temperature rises, then the water level in the coastal areas rises. The logic string in this case would go like this: People are rewarded Æ People change their lifestyle (might or might not happen-as we do not know for certain that people would change their lifestyle if they are rewarded.) We cannot conclude anything about whether the temperature rises or does not as we do not know whether people changed their lifestyle, since we do not know about the temperature movement we can conclude nothing about the rise in water level in coastal areas. Thus, the conclusion given in H is uncertain in this case, and it is not something we can definitely conclude. Thus, this option is also rejected. The following checking structure would work for option (c). The statements in option (c) are: E, F, G, H and B. Amongst these, G and H are again the cause and effect statements as they are the only events amongst the statements given. Hence, the cause-effect relationship we need to test is: People are rewarded (leading to) Æ Water level in the coastal areas does not rise, under the conditions specified by the statements E, F, B. B states: People change their lifestyle only if they are rewarded. Note here that this means that in case people are rewarded, they may change their lifestyle but it is not sure whether they would change their lifestyle if they are rewarded. What is sure is that if they are not rewarded they would not change their lifestyle (as explained above). F states: Unless people change their lifestyle, temperature rises. E states: Whenever the water level in the coastal areas rises, the temperature rises. The logic string in this case would go like this: People are rewarded Æ Statement B-People change their lifestyle (might or might not happen-as we do not know for certain that people would change their lifestyle if they are rewarded.) Æ Statement F-We cannot conclude anything about whether the temperature rises or does not as we do not know whether people changed their lifestyle. Æ Statement E is totally irrelevant in this case and does not fit into the logic string. Thus, the conclusion given in H is uncertain in this case, and it is not something we can definitely conclude. Thus, this option is also rejected. Hence, option (d) is the correct answer.
- Explanation :
Like the previous question, the first thing you should notice in this question, is that out of the given 8 statements in this question, only statements G and H are event based statements. The other statements specify conditions and are in the following formats: (i) If A then B- which means that if A occurs then B occurs; (iv) Only if A then B-which means that A causes B and also that A is the only cause that leads to B. (vi) Unless not A, B-which means that B would happen unless A does not happen. From this point we can move into the options and check the logical consistency of the statements in each option in much the same way as we did it in the previous question. Checking option (a): The statements which are part of this option: C, F, G, B and H. Again since G and H are the only events in this list we will essentially test the cause-effect relationship: Vina Dances Æ (results in) the concert is successful. And we need to see if this turns out to be a logical conclusion under the conditions specified by B, C and F. B states: If Kumar sings, then the audiences dance. C states: Unless the audience do not dance, the concert will be successful. F states: Kumar sings only if Vina dances. Now the logic string that can be built based on these conditions is: Vina Dances Æ Statement F-Whether Kumar sings is uncertain (check the logic of the statement: You will succeed only if you work hard.)Æ Statement B-Thus, whether audience would dance is uncertain because they dance if Kumar sings Æ Statement C-The concert being successful is not something we can definitely say. Thus, this option is rejected. We would check options (b) and (c) similarly. Checking option (b), the events described in this option give us the logic: Vina dances Æ (leads to) The concert is successful and we need to test whether statements A, C, F justify this conclusion. A states: If Kumar sings, then the audience sleep. C states: Unless the audience do not dance, the concert will be successful. F states: Kumar sings only if Vina dances. Now the logic string that can be built based on these conditions is: Vina Dances Æ Statement F-Whether Kumar sings is uncertain (check the logic of the statement: You will succeed only if you work hard)Æ Statement A-Thus, whether audience would sleep or dance or do not dance is uncertain because they sleep if Kumar sings Æ Statement C-The concert being successful is not something we can definitely say. Thus, this option is rejected. Checking option (c), the events described in this option give us the logic: Vina dances Æ (leads to) The concert is successful and we need to test whether statements B, C, E justify this conclusion. B states: If Kumar sings, then the audience dance. C states: Unless the audience do not dance, the concert will be successful. E states: If Vina dances, Kumar sings. Now the logic string that can be built based on these conditions is: Vina Dances Æ Statement E-Kumar sings is certainÆ Statement B-If Kumar sings, then the audiences dance, so the audience would dance, since Kumar is singing Æ Since the audience is dancing, the concert would be successful. Thus, this option is correct. Option (c) is the correct answer.
Ans .
(d) None of the above
Ans .
(c) E, C, G, B and H
Directions for Questions 3 and 5: These questions are based on the data given below. There are only four members of a family viz., A, B, C and D and there is only one couple among them. When asked about their relationships, following were their replies: a. A: B is my son. D is my mother. c. C: D is my mother-in-law. A is my daughter. d. D: A is my grand-daughter. B is my daughter-in- law.
- Explanation :
The mapping of the 4 statements can be shown as follows: A's Statement:
 B's Statement:
B's Statement:
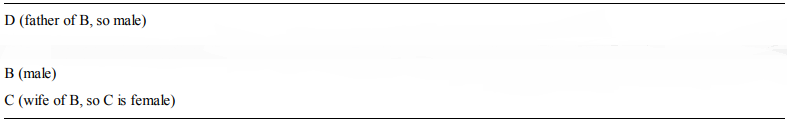 C's Statement:
C's Statement:
 D's statement:
D's statement:
 In order to find out who is always speaking the truth you need to think of a couple of things. The first
one is that, the relationship between B and C has to be clearly established, otherwise the answer to
the second question in this set would become 'cannot be determined' an option that does not exist in
this question.
If you were to use the relationship grids drawn above, it is clear that only B's or D's statements could
both be true as they are the only ones defining a clear relationship between B and C. By a similar
logic we need information about the relationships of each of the 4 people, from the statements of the
person who speaks both statements true in order to test the truth of the options in the third question in
the set. If we look at the statements of B, it is clear that although we do get a relationship between B,
C and D in this case, we are not able to place A. Thus, we cannot assume both statements of B to be
true.
This can only mean that both the statements of D must be true, as D's statements clearly identify the
relationships between A, B, C and D.
D always speaks the truth. Option (d) is correct.
In order to find out who is always speaking the truth you need to think of a couple of things. The first
one is that, the relationship between B and C has to be clearly established, otherwise the answer to
the second question in this set would become 'cannot be determined' an option that does not exist in
this question.
If you were to use the relationship grids drawn above, it is clear that only B's or D's statements could
both be true as they are the only ones defining a clear relationship between B and C. By a similar
logic we need information about the relationships of each of the 4 people, from the statements of the
person who speaks both statements true in order to test the truth of the options in the third question in
the set. If we look at the statements of B, it is clear that although we do get a relationship between B,
C and D in this case, we are not able to place A. Thus, we cannot assume both statements of B to be
true.
This can only mean that both the statements of D must be true, as D's statements clearly identify the
relationships between A, B, C and D.
D always speaks the truth. Option (d) is correct. - Explanation :
The mapping of the 4 statements can be shown as follows: A's Statement:
 B's Statement:
B's Statement:
 C's Statement:
C's Statement:
 Dӳ statement:
Dӳ statement:
 In order to find out who is always speaking the truth you need to think of a couple of things. The first
one is that, the relationship between B and C has to be clearly established, otherwise the answer to
the second question in this set would become 'cannot be determined'an option that does not exist in
this question.
If you were to use the relationship grids drawn above, it is clear that only B's or D's statements could
both be true as they are the only ones defining a clear relationship between B and C. By a similar
logic we need information about the relationships of each of the 4 people, from the statements of the
person who speaks both statements true in order to test the truth of the options in the third question in
the set. If we look at the statements of B, it is clear that although we do get a relationship between B,
C and D in this case, we are not able to place A. Thus, we cannot assume both statements of B to be
true.
This can only mean that both the statements of D must be true, as D's statements clearly identify the
relationships between A, B, C and D.
B is the wife of C. Option (c) is correct.
In order to find out who is always speaking the truth you need to think of a couple of things. The first
one is that, the relationship between B and C has to be clearly established, otherwise the answer to
the second question in this set would become 'cannot be determined'an option that does not exist in
this question.
If you were to use the relationship grids drawn above, it is clear that only B's or D's statements could
both be true as they are the only ones defining a clear relationship between B and C. By a similar
logic we need information about the relationships of each of the 4 people, from the statements of the
person who speaks both statements true in order to test the truth of the options in the third question in
the set. If we look at the statements of B, it is clear that although we do get a relationship between B,
C and D in this case, we are not able to place A. Thus, we cannot assume both statements of B to be
true.
This can only mean that both the statements of D must be true, as D's statements clearly identify the
relationships between A, B, C and D.
B is the wife of C. Option (c) is correct.
- Explanation :
The mapping of the 4 statements can be shown as follows: A's Statement:
 B's Statement:
B's Statement:
 C's Statement:
C's Statement:
 D's statement:
D's statement:
 In order to find out who is always speaking the truth you need to think of a couple of things. The first
one is that, the relationship between B and C has to be clearly established, otherwise the answer to
the second question in this set would become 'cannot be determined' an option that does not exist in
this question.
If you were to use the relationship grids drawn above, it is clear that only B's or D's statements could
both be true as they are the only ones defining a clear relationship between B and C. By a similar
logic we need information about the relationships of each of the 4 people, from the statements of the
person who speaks both statements true in order to test the truth of the options in the third question in
the set. If we look at the statements of B, it is clear that although we do get a relationship between B,
C and D in this case, we are not able to place A. Thus, we cannot assume both statements of B to be
true.
This can only mean that both the statements of D must be true, as D's statements clearly identify the
relationships between A, B, C and D.
Once we realise that D is always true, we also realise that both of A's statements must be
false. Also, if D's statements are true, A is B's daughter. Option (d) is hence the correct
answer.
In order to find out who is always speaking the truth you need to think of a couple of things. The first
one is that, the relationship between B and C has to be clearly established, otherwise the answer to
the second question in this set would become 'cannot be determined' an option that does not exist in
this question.
If you were to use the relationship grids drawn above, it is clear that only B's or D's statements could
both be true as they are the only ones defining a clear relationship between B and C. By a similar
logic we need information about the relationships of each of the 4 people, from the statements of the
person who speaks both statements true in order to test the truth of the options in the third question in
the set. If we look at the statements of B, it is clear that although we do get a relationship between B,
C and D in this case, we are not able to place A. Thus, we cannot assume both statements of B to be
true.
This can only mean that both the statements of D must be true, as D's statements clearly identify the
relationships between A, B, C and D.
Once we realise that D is always true, we also realise that both of A's statements must be
false. Also, if D's statements are true, A is B's daughter. Option (d) is hence the correct
answer.
Ans .
(d) D
Ans .
(c) Wife
Ans .
(d) B's daughter always tells lies.
Directions for Questions 6 and 8: These questions are based on the following information. A cube of 7 cm ¥, 7 cm ¥, 7 cm is kept in the corner of a room and painted in three different colours, each face in one colour. The cube is cut into 343 smaller but identical cubes.
- Explanation :
The basic figure for this situation would look as shown below with the two lateral sides and the front face exposed for painting, while the other three surfaces would be covered by the wall or the ground, and hence would not be accessible for painting.
There would be a total of 49 smaller cubes on each of the three exposed surfaces which would be painted. Out of these, if we count 49 smaller cubes on the top exposed surface, then in the lateral surfaces we would get an additional 42 and 36 cubes respectively which would be painted. Thus a total of 127 smaller cubes would be painted and hence, 216 cubes out of 342 would not be painted even on one side. Alternately, you can think of this as 6 ¥, 6 ¥, 6 = 216 as if we remove the top layer on all three lateral surfaces, we would get a total of 216 smaller cubes which would get uncovered. Option (d) is the correct answer.
- Explanation :
The basic figure for this situation would look as shown below with the two lateral sides and the front face exposed for painting, while the other three surfaces would be covered by the wall or the ground, and hence would not be accessible for painting.
There would be a total of 49 smaller cubes on each of the three exposed surfaces which would be painted. Out of these, if we count 49 smaller cubes on the top exposed surface, then in the lateral surfaces we would get an additional 42 and 36 cubes respectively which would be painted. Thus a total of 127 smaller cubes would be painted and hence, 216 cubes out of 342 would not be painted even on one side. The cubes on the three edges of the intersection of the exposed surfaces would be painted on two or more surfaces. Thus, on each of the exposed surfaces there would be 36 cubes, which would be painted only on one side. Thus, the total number of cubes, which would be painted only on one side would be equal to 36 + 36 + 36 = 108. Option (a) is correct.
- Explanation :
The basic figure for this situation would look as shown below with the two lateral sides and the front face exposed for painting, while the other three surfaces would be covered by the wall or the ground, and hence would not be accessible for painting.
There would be a total of 49 smaller cubes on each of the three exposed surfaces which would be painted. Out of these, if we count 49 smaller cubes on the top exposed surface, then in the lateral surfaces we would get an additional 42 and 36 cubes respectively which would be painted. Thus a total of 127 smaller cubes would be painted and hence, 216 cubes out of 342 would not be painted even on one side. The cubes on the three edges of the intersection of the exposed surfaces would be painted on two or more surfaces. At most two faces painted means we need to exclude the smaller cube/s which have three faces painted. In this situation there would be only 1 cube which would have 3 faces painted. Hence the correct answer would be 343 - 1 = 342. Option (b) is correct.
Ans .
(d) 216
Ans .
(a) 108
Ans .
(b) 342
Directions for Questions 9 and 10: Amit was driving in New Town, where all roads run either north-south or east-west form a grid. Roads were at a distance of 1 km from each other and parallel to each other.
- Explanation :
The movement, which would occur in this case, would look as follows:
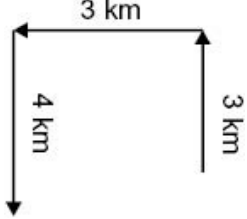 From the figure it is clear that if he wants to go back to the starting point he needs to travel 1
km north and 3 km east. Thus, the route described in II gets him back to his starting point. The
other routes specified in (I) and (III) do not get him back to the starting point.
From the figure it is clear that if he wants to go back to the starting point he needs to travel 1
km north and 3 km east. Thus, the route described in II gets him back to his starting point. The
other routes specified in (I) and (III) do not get him back to the starting point. - Explanation :
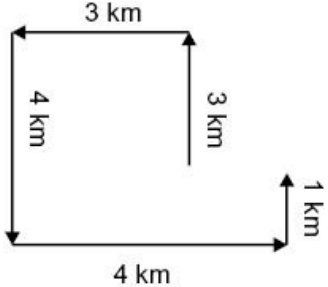
In this case his movement would be as follows: From the figure it is clear that he would be 1 km from his starting point
Ans .
(b) II only
Ans .
(c) 1 km
Directions for Questions 11 and 15: Refer to the following data and answer the questions that follow: A numerical machine accepts two values X and Y. Then it updates these values as X = XY and Y = Y + 1 in every step. The machine stops at X = N.
- Explanation :
In order to solve this set of questions you need to build a table showing how the values of X and Y move in every iteration. Questions 51 to 54 will be solved based on the following table:
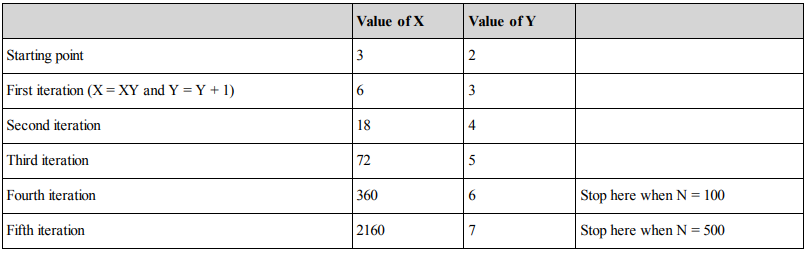 The answers can then be interpreted from this table
The machine would stop after 4 iterations. Option (c) is correct
The answers can then be interpreted from this table
The machine would stop after 4 iterations. Option (c) is correct
- Explanation :
The final value of X is 360. Option (d) is correct
- Explanation :
The final value of Y (after the fourth iteration when X crosses 100) is 6. Option (c) is correct.
- Explanation :
There would be an additional iteration in this case (the fifth one) and the value of X would land at 2160. Option (d) is correct
- Explanation :
The following table would define the iterations in this case:
From the above table it is clear that the fourth iteration would be necessitated only if the value of N is 121 or more than that. From amongst the options the minimum value of N possible is 300 for the fourth iteration to take place and the value of Y to end at 7.
Ans .
(c) 4
Ans .
(d) 360
Ans .
(c) 6
Ans .
(d) 2160
Ans .
(a) 300
Directions for Questions 16 and 20: Refer to the following statements and answer the questions: Seven students Priya, Ankit, Raman, Sunil, Tony, Deepak and Vicky take a series of tests. No two students get similar marks. Vicky always scores more than Priya. Priya always scores more than Ankit. Each time either Raman scores the highest and Tony gets the least, or alternatively Sunil scores the highest and Deepak or Ankit scores the least.
- Explanation :
The following are the basic possibilities that emerge in this case based on the possible outcomes given for who comes first and who comes last: Possibility 1
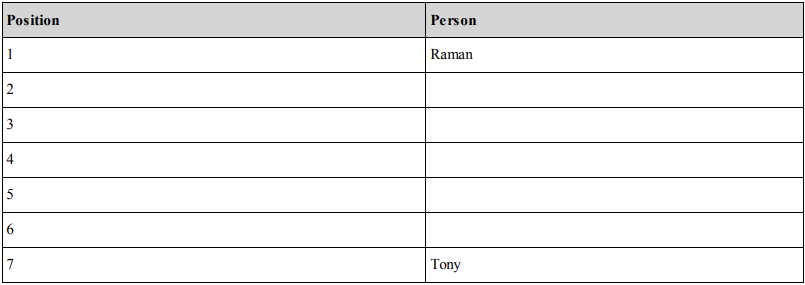 OR POSSIBILITY 2:
OR POSSIBILITY 2:
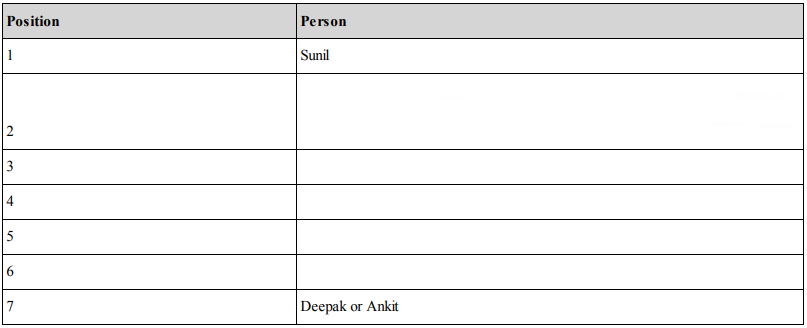 Besides we also know that Vicky > Priya > Ankit.
Based on this initial thought we can move into the questions and the process for solving from this
point would be to add the information given in the question to the respective possibilities and see
what cases emerge, and hence what conclusions emerge
If Sunil is ranked sixth, it is clear that we are moving to Possibility 1:
The table structure becomes:
Besides we also know that Vicky > Priya > Ankit.
Based on this initial thought we can move into the questions and the process for solving from this
point would be to add the information given in the question to the respective possibilities and see
what cases emerge, and hence what conclusions emerge
If Sunil is ranked sixth, it is clear that we are moving to Possibility 1:
The table structure becomes:
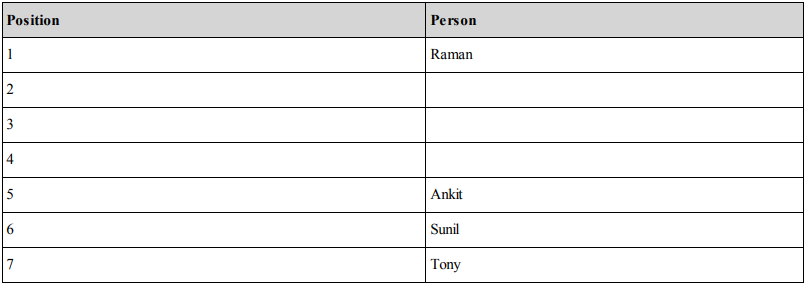 This leaves us with Vicky > Priya and also Deepak to place in the above grid. Now clearly,
the first three options can be rejected because Vicky has to be placed 2nd or 3rd and hence
saying he finished fourth or fifth cannot be true. Thus, option (a) is rejected. Similarly, Raman
has to be first in this scenario and thus option (b) is also not true. Option (c) is also not true as
Tony is compulsorily ranked 7th in this case. Thus, option (d) is correct as Deepak can be
ranked 3rd or 4th.
Option (d) is the correct answer.
This leaves us with Vicky > Priya and also Deepak to place in the above grid. Now clearly,
the first three options can be rejected because Vicky has to be placed 2nd or 3rd and hence
saying he finished fourth or fifth cannot be true. Thus, option (a) is rejected. Similarly, Raman
has to be first in this scenario and thus option (b) is also not true. Option (c) is also not true as
Tony is compulsorily ranked 7th in this case. Thus, option (d) is correct as Deepak can be
ranked 3rd or 4th.
Option (d) is the correct answer.
- Explanation :
From the above analysis it is clear that if Raman is ranked first we are clearly talking about the first possibility and hence, Vicky cannot be ranked lower than 3rd as he has to be ranked either 2nd or 3rd. Option (b) is correct.
- Explanation :
In this case we are told that Ankit is ranked 2nd. However looking at the original possibilities given to us we can clearly realise that this is not possible. Hence, the ideal answer would be that this is not possible. However, none of the options tells us that. Hence, option (d) is the correct answer
- Explanation :
If Sunil is ranked second we are moving to possibility 1: The table structure becomes: Possibility 1
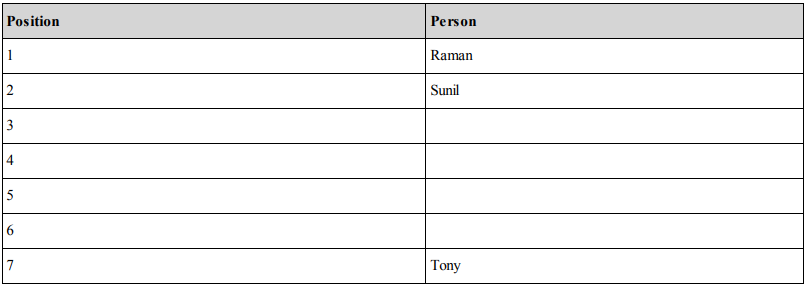 We also know that Vicky > Priya > Ankit.
In this scenario,
Option (b): Vicky > Sunil is not possible (option (b) is rejected).
Option (c): Priya > Raman is also not possible. (option (c) is rejected).
Option (d): Priya > Vicky is also not possible as it is given clearly that Vicky gets more than
Priya.
Only the first option is possible as we can have the following arrangement:
We also know that Vicky > Priya > Ankit.
In this scenario,
Option (b): Vicky > Sunil is not possible (option (b) is rejected).
Option (c): Priya > Raman is also not possible. (option (c) is rejected).
Option (d): Priya > Vicky is also not possible as it is given clearly that Vicky gets more than
Priya.
Only the first option is possible as we can have the following arrangement:

- Explanation :
If Vicky is ranked fifth, since we need to compulsorily fit Priya and Ankit below Vicky in that order we will have to move to the second possibility table: Possibility 2
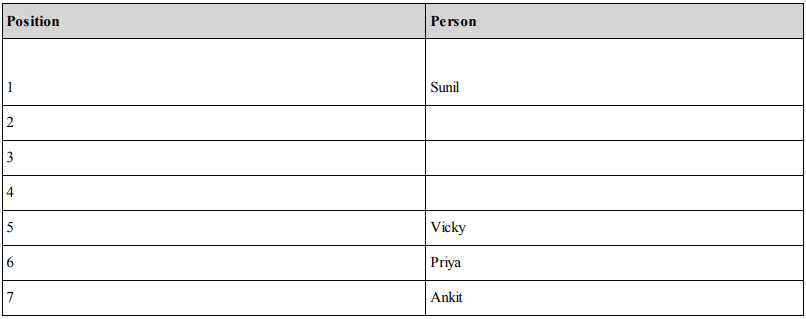 In this situation, the only 'must true' option is the one which states that Sunil scores the
highest.
Option (a) is correct
In this situation, the only 'must true' option is the one which states that Sunil scores the
highest.
Option (a) is correct
Ans .
(d) Deepak is ranked third or fourth.
Ans .
(b) Third
Ans .
(d) None of these
Ans .
(a) Deepak gets more than Vicky.
Ans .
(a) Sunil scores the highest.
Ans .
(c) 35% of people favour party "Z".
- Explanation :
The conclusion drawn in the passage talks about Party Z being likely to win the election. Obviously if we know that only 35% of the people favour party Z (as stated in option (c)), party Y would be expected to win the election as the estimates for how many people support party Y varies from 40% (at worst) to 46% (at best). Even, in the worst case scenario for Party Y, Party Z would still not be likely to win the next election. Thus, option (c) seriously weakens the conclusion.
Ans .
(d) Much of the quarterly increase in the price level was due to a summer drought effect on food price.
- Explanation :
The stock markets find their levels based on long term expectations of results of businesses in the economy. Obviously, if it is known that much of the inflation was the result of the rise in food prices due to a summer drought (which in essence is a short term effect), the stock markets would not need to panic and change their levels drastically, thereby being steady in the short run. Thus, option (d) is the best explanation for the reaction of the stock market.
Directions for Question 23: Pick up the appropriate analogy.
- Explanation :
The original relationship between birth: dirge signifies the beginning and the end of life. Birth being the start of life, dirge which means a funeral hymn or lament signifies the end of life. The same relationship is exhibited in the pair Marriage: alimony, where marriage signifies the start of a relationship and alimony is something that signals the end of the relationship.
Ans .
(c) marriage : alimony
Ans .
(d) During weather my dog suffers from fleas more than during cooler weather. Therefore, fleas must thrive in a warm environment.
- Explanation :
The argument in the question is based on the premise that just because the city's beaches are the most overcrowded in the state, so it must be true that beautiful beaches attract people. The reasoning is akin to making a generic conclusion about something based on one observation. Similar reasoning is shown by option (d) because it uses a similar kind of logic to make a conclusion. The whole conclusion is based on one fact, viz: just because my dog suffers more fleas during hot weather, it follows that fleas must thrive in a warm environment.
Ans .
(d) there are at least some industries run entirely by self-employed industrialists that are not underground industries.
- Explanation :
The conclusion in option (d) is the most valid in this case because the question clearly states that all underground industries are not included in national productivity measures and that there are some industries run by self-employed industrialists, which are included in national productivity measures. Obviously this means that there are at least some industries run entirely by self-employed industrialists that are not underground industries (as they are included in national productivity measures).
Ans .
(c) The argument is built upon hidden assumptions.
- Explanation :
The argument is directly linking 'Not receiving a violation from the Federal Aviation' to being a good pilot. Thus, it is based on a hidden assumption which can be stated as not receiving a violation from Federal Aviation means the pilot is a good pilot.
Ans .
(c) a general conclusion based on a specific example.
- Explanation :
The argument is a general conclusion (about a large topic) based on a specific example of 1 individual. Thus, option (c) is correct.
Ans .
(d) 6
- Explanation :
The value of the middle number in every row is equal to half the sum of the other numbers in the row. This can be verified by looking at any of the first four rows. In the first row \( \frac{4+2}{2} \) = 3; a similar logic exists for the other rows. The missing number is \( \frac{9+3}{2} \) = 6.
Ans .
(c) If the restrictions against advertisements that do not specify fee arrangements is removed, more lawyers will advertise their services.
- Explanation :
The cause-effect relationship specified in the question, tells us that: Fewer restrictions on advertising of legal services AE More lawyers advertise their services AE Lawyers who specify a specific service generally charge less for the service. Based on this reasoning, the author is concluding that: If restrictions on advertising specifying fee arrangements are removed AE lower legal costs. If this were true, it would happen only if more lawyers end up advertising their services. Option (c) states exactly that and hence is the correct answer.
Ans .
(d) Most lawyers who advertise specific services do not lower their fees for those services when they begin to advertise.
- Explanation :
If the condition stated in option (d) were to be true; that the lawyers who begin to advertise do not lower their fees, naturally the conclusion that there would be a drop in legal costs would be weakened most seriously. Hence, option (d) is the correct answer.