-
Chapter 18: DECISION MAKING
Introduction
Based on the data that is provided the student has to verify whether the question can be answered. The questions in this section are of the type: Selection of a candidate / allotment to a member.
Problem and Solution
Q. Following are the criteria for selecting a marketing officer by a company.
The candidate must :
(1) be a graduate with at least 50% marks.
(2) have secured at least 40% marks in the written test.
(3) not be less than 24 years and more than 29 years as on 10th October, 1997.
(4) should have work experience of at least two years as an officer.
However, if a candidate :
(5) fulfills all other criteria except at (4) above but has a diploma in Marketing Management, his/her case is to be referred to General Manager, Marketing.
(6) fulfills all other criteria except at (3) above but has worked as Marketing Officer at least for three years, his/her case is to be referred to Director, Marketing.
Based on the above criteria and the information given in each of the following questions, you have to take the decision in regard to each case. You are not to assume anything. These cases are given to you as on 10th October, 1997.
Mark answer (a) if the candidate is to be appointed; mark answer (b) if the candidate is not to be appointed; mark answer (c) if the data given are not sufficient to take decision; mark answer (d) if to be referred to General Manager — Marketing; and mark answer (e) if to be referred to Director — Marketing.
1. Amit Khanna, born on 5th June, 1973, has done his post-graduation in Marketing Management with first class. He has secured 50% marks in the written test. He has been working in an organization as a Marketing Officer for the last four years.
A. Eligible
2. Rohit Verma has been working in an organization as Officer for the last ten years. His date of birth is 17th February, 1964. He has secured 60% marks in the degree examination and 40% marks in the written test.
A. Age criteria not met but no mention of work experience as marketing officer for 3 years so data insufficient.
3. Manju Sharma is a first class graduate and has done a diploma in Marketing Management. She has secured 50% marks in the written test. She was 23 years old as on 5th September, 1996.
A. Refer to General manager - marketing
4. Nitin Narang was born on 25th August, 1975. He has secured 60% and 50% marks in graduation and in the written test, respectively. He has been working in an organization as Officer for the last four years.
A. Doesn't satisfy age criteria and the so needs 3 years experience as marketing officer in an organization which isn't mentioned so insufficient data.
5. Suman Malhotra is a graduate with first class and has secured 60% marks in the written test. She has been working as an Officer for the last three years. She was born on 20th May, 1972.
A. Eligible.
Chart Problems
Q. In an examination there are five heads of passing, each of 100 marks :
(I ) Paper 1 (II ) Paper 2 (III ) Paper 3 (IV) Practicals (V) Year's Work
The passing marks are 40 except for Practicals (IV) for which the passing marks are 50,
A candidate who fails may appear again in subsequent examination, when he can claim exemption from appearing in the heads of passing in which he has secured 10 marks more than the passing marks. A candidate who has failed in the head of passing year's work has to undergo the whole course afresh.
Up to 3 grace marks may be given in each of not more than three heads of passing. A candidate who secures more than 50% of the total marks may be given up to 5 grace marks in not more than one head of passing. In exceptional cases, the Board of Examiners may give up to 7 grace marks in not more than one head of passing. A candidate who has appeared with exemption in one or more heads of passing will not be entitled to any grace marks. A candidate who passes with 75% or more marks at one and the same examination will be declared to have passed with distinction.
The marks obtained by candidates P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X and Y are given below. In each case, give answer (a) if the candidate passes; give answer (b) if the candidate passes with Distinction; give answer (c) if the candidate has failed; give answer (d) if the candidate passes with grace marks and give answer (e) if the case needs to be referred to the Board of Examiners. (f)
A 1. Candidate S has got distinction in II, IV, V
A 2. Candidate passes with 7 grace marks.
A 3. Passes in IV with 2 grace marks.
A 4. Candidate passes with 6 grace marks.
A 5. Candidate fails as he has failed in more than 3 subjects.
A 6. Candidate passes
A 7. Candidate passes with 6 grace marks.
A 8. Candidate gets more than 50% of total marks and so gets 5 grace marks.
A 9. The candidate passes in each of the heads with more than 75% marks.
A 10. Fails as he isn't eligible for grace marks.
Decision Making Case -1
You are asked to advise a client on a business decision. The client wants to open a training center for training high school teachers, college teachers and professional courses teachers. The cost involved in setting up such a venture are as follows: - For high school training ( Rs.2 lakh per annum and Rs. 1000 per candidate), for high school and college teachers ( Rs. 3.2 lakh per year and rs. 750 per candidate) and for all three (Rs. 5 lakh per year and Rs. 500 per candidate)
Q.For how many candidates shall the training center incur same cost for training high school and high school and college teachers.
Q.For how many candidates shall the training center incur same cost for training high school, college and professional teachers and high school and college teachers.
Q.For how many candidates shall the training center incur same cost for training high school and all three teachers.
Q.What is profit or loss if the client sets up training center for all three teachers and charges Rs. 1250 per candidate in first year.
Q.What is profit % in first year for above case.
| 1- 480 | 2- 720 |
| 3- 600 | 4- 4 lakh |
| 5- 36.66% |
Decision Making Case - 2
In 2004 the hotel industry generated revenue of Rs. 50 billion as 200 million hotel users (about 20% of India's population) were there and in 2008 the hotel industry generated 150 billion in revenue as hotel users grew to 560 million or half the population.
Q.What is India's population in 2004.
Q.What is the growth rate of population from 2004-2008
Q.What was the average growth in % terms of hotel users from 2004-2008.
Q.What is % growth in hotel industry revenues in that period
Q.A developed country has 50% population that can afford hotels so was India developed in 2007?
| 1- 100 crore | 2- 3% |
| 3- 180% | 4- 200% |
| 5- cant say |
Decision Making Case - 3
1/5th of India's population and 1/3rd of India's illiterates live in bihar and Odisa. 1/10 of infants die at birth and same number before 5 years of age. More than 2/3rds of births are not attended by medical staff. Almost 90% of under 5 deaths are due to malnutrition. Those who survive the first five years, 1/3 rd of those work as child laborers and half the rest go to school. Only 40% of those reach 5th standard. India has 30% of its children under 16 working as child laborers. Odisa and bihar have 1/3rd of Indias child laborers and 1/15th of India's population is of child laborers. In Odisa and bihar out of 100 children enrolled in schools only 32 are girls. And out of 100 who attend 10th only 10 are girls. 38/100 Indian women are lierate compared to 57% males. 90 crore was Indias population in 1998 and girl to boy ratio ws 9:10.
Q.What % of infants in odisa and bihar attend class 5.
Q.What is the number of child laborers in India in 1998
Q.How many children out of 100 work as child laborers in odisa and bihar
Q.What % of girl children enrolled in school reach std 10 in odisa and bihar
Q.1998 data says literates in kerela exceeded those in odisa and bihar by
Q.1998 data says literates in India are
Q.1998 data says illiterates in Odisa and bihar is
| 1- 10.66 | 2- 6 crore |
| 3- 27 | 4- data insufficient |
| 5- insufficient | 6- 43.2 crore |
| 7- 15.6 crore |
Decision Making Case - 4
A company has 6 spinning machines, 10 weaving and 5 dyeing. Each machine works for 10 hours and a fabric goes through spinning, weaving and dyeing. One unit of fabric X needs 40 mins spinning, 2 hrs weaving and 30 mins dyeing. Fiber Y needs 60 mins spinning, 30 mins weaving and 60 mins dyeing
Q.In a day how many units of fiber Y are completed
Q.20 units fiber y are made in a day so how many units fiber x can be made on same day
Q.if the fiber y is made of 30 units then on that day how many hours machines were idle.
Q.If one more dyeing machine is added then how many units of fiber x can be made on that day
Q.if we want to manufacture only fiber x and can purchase only one machine. which should we buy to get maximum increase in production
Q.if we want to manufacture only fiber y and can purchase only one machine. which should we buy to get maximum increase in production
| 1- 30 | 2- 45 |
| 3- 135 | 4- 0 |
| 5- weaving | 6- dyeing |
Read and answer
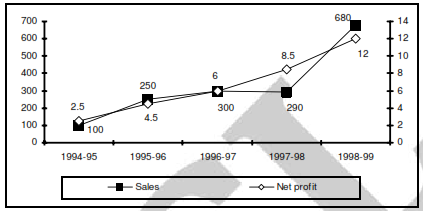
The figure below represents sales and net profit in Rs. crore of IVP Ltd. for five years from 1994-95 to 1998-99. During this period the sales increased from Rs. 100 crore to Rs. 680 crore. Correspondingly, the net profit increased from Rs. 2.5 crore to Rs. 12 crore. Net profit is defined as the excess of sales over total costs.
Q. The highest percentage of growth in sales, relative to the previous year, occurred in
1995-96
1996-97
1997-98
1998-99
Ans . A
Q. The highest percentage growth in net profit, relative to the previous year, was achieved in
1998-99
1997-98
1996-97
1995-96
Ans . D
Q. Defining profitability as the ratio of net profit to sales, IVP Ltd., recorded the highest profitability in
1998-99
1997-98
1994-95
1996-97
Ans . B
Q. With profitability as defined in question 137, it can be concluded that
profitability is non-decreasing during the five years from 1994-95 to 1998-99
profitability is non-increasing during the five years from 1994-95 to 1998-99.
profitability remained constant during the five years from 1994-95 to 1998-99.
None of the above
Ans . D
Read and answer
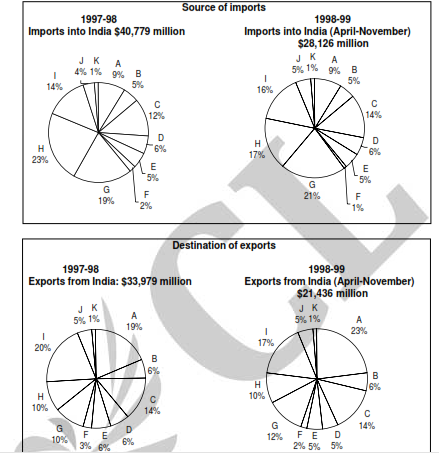
Consider the information provided in the figure below relating to India’s foreign trade in 1997-98 and the first
eight months of 1998-99. Total trade with a region is defined as the sum of exports and imports from that
region. Trade deficit is defined as the excess of imports over exports. Trade deficit may be negative.
A. USA B. Germany C. Other EU
D. UK E. Japan F. Russia
G. Other East European countries H. OPEC I. Asia
J. Other LDCs K. Others
Q. What is the region with which India had the highest total trade in 1997-98?
USA
Other EU countries
OPEC
Others
Ans . C
Q. In 1997-98 the amount of Indian exports, million US dollars, to the region with which India had the lowest total trade, is approximately
750
340
220
440
Ans . B
Q. In 1997-98, the trade deficit with respect to India, billion US dollars, for the region with the highest trade deficit with respect to India, is approximately equal to
6.0
3.0
4.5
7.5
Ans . A
Q. What is the region with the lowest trade deficit with India in 1997-98?
USA
Asia
Others
Other EU countries
Ans . A
READ AND ANSWER
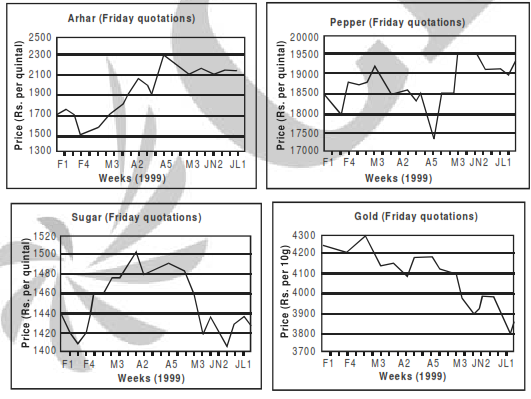
These questions are based on the price fluctuations of four commodities — arhar, pepper, sugar and gold during February-July 1999 as described in the figures below.
Q. Price change of a commodity is defined as the absolute difference in ending and beginning prices expressed as a percentage of the beginning. What is the commodity with the highest price change?
Arhar
Pepper
Sugar
Gold
Ans . A
Q. Price volatility (PV) of a commodity is defined as follows: PV = (Highest price during the period – Lowest price during the period)/Average price during the period. What is the commodity with the lowest price volatility?
Arhar
Pepper
Sugar
Gold
Ans . C
Q. Mr X, a fund manager with an investment company invested 25% of his funds in each of the four commodities at the beginning of the period. He sold the commodities at the end of the period. His investments in the commodities resulted in
17% profit
5.5% loss
No profit, no loss
5.4% profit
Ans . D
Q. The price volatility(PV) of the commodity with the highest PV during the February-July period is approximately equal to
3%
40%
20%
12%
Ans . B
Read and answer
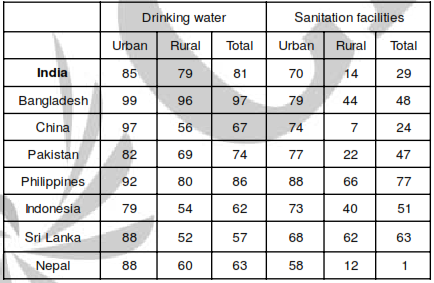
Population covered by drinking water and sanitation facilities. Percentage coverage. Country A is said to dominate B or A > B if A has higher percentage in total coverage for both drinking water and sanitation facilities, and, B is said to be dominated by A, or B < A. A country is said to be on the coverage frontier if no other country dominates it. Similarly, a country is not on the coverage frontier if it is dominated by at least one other country.
Q. Which countries are the countries on the coverage frontier?
India and China
Sri Lanka and Indonesia
Philippines and Bangladesh
Nepal and Pakistan
Ans . C
Q. Which of the following statements are true?
A. India > Pakistan and India > Indonesia B. India > China and India > Nepal
C. Sri Lanka > China D. China > Nepal
A and C
B and D
A, B and C
B, C and D
Ans . B
Q. Using only the data presented under ‘sanitation facilities’ columns, it can be concluded that rural population in India, as a percentage of its total population is approximately
76
70
73
Cannot be determined
Ans . C
Q. Again, using only the data presented under ‘sanitation facilities’ columns, sequence China, Indonesia and Philippines in ascending order of rural population as a percentage of their respective total population. The correct order is
Philippines, Indonesia, China
Indonesia, China, Philippines
Indonesia, Philippines, China
China, Indonesia, Philippines
Ans . A
Q. India is not on the coverage frontier because
A. it is lower than Bangladesh in terms of coverage of drinking water facilities.
B. it is lower than Sri Lanka in terms of coverage of sanitation facilities.
C. it is lower than Pakistan in terms of coverage of sanitation facilities.
D. it is dominated by Indonesia.
A and B
A and C
D
None of these
Ans . D
READ AND ANSWER
Assume that the average monthly exports from India and imports to India during the remaining four months of 1998-99 would be the same as that for the first eight months of the year.
Q. What is the region to which India’s exports registered the highest percentage growth between 1997-98 and 1998-99?
Other East European countries
USA
Asia
Exports have declined, no growth
Ans . B
Q. What is the percentage growth rate in India’s total trade deficit between 1997-98 and 1998-99?
43
47
50
40
Ans . B
Directions for questions 154 and 155: Answer the questions based on the following information.
These relate to the above table with the additional provision that the gap between the population coverages of ‘sanitation facilities’ and ‘drinking water facilities’ is a measure of disparity in coverage.
Q. The country with the most disparity in coverage of rural sector is
India
Bangladesh
Nepal
None of these
Ans . A
Q. The country with the least disparity in coverage of urban sector is
India
Pakistan
Philippines
None of these
Ans . C
Each question is followed by two statements, I and II. Answer each question using the following instructions.
Mark the answer as
(a) if the question can be answered by one of the statements alone, but cannot be answered by
using the other statement alone.
(b) if the question can be answered by using either statement alone.
(c) if the question can be answered by using both the statements together, but cannot be answered
by using either statement alone.
(d) if the question cannot be answered even by using both statements together.
Q. Consider three real numbers, X, Y and Z. Is Z the smallest of these numbers?
I. X is greater than at least one of Y and Z.
II. Y is greater than at least one of X and Z.
A
B
C
D
Ans . C
Q. Let X be a real number. Is the modulus of X necessarily less than 3?
I. X(X + 3) < 0
II. X(X – 3) > 0
A
B
C
D
Ans . A
Q. How many people are watching TV programme P?
I. Number of people watching TV programme Q is 1,000 and number of people watching both the
programmes P and Q, is 100.
II. Number of people watching either P or Q or both is 1,500.
A
B
C
D
Ans . C
Q. △ PQR has ∠ PRQ = 90°. What is the value of PR + RQ?
I. Diameter of the inscribed circle of the △ PQR is equal to 10 cm.
II. Diameter of the circumscribed circle of the △ PQR is equal to 18 cm.
A
B
C
D
Ans . C
Q. Harshad bought shares of a company on a certain day, and sold them the next day. While buying
and selling he had to pay to the broker 1% of the transaction value of the shares as brokerage. What
was the profit earned by him per rupee spent on buying the shares?
I. The sales price per share was 1.05 times that of its purchase price.
II. The number of shares purchased was 100.
A
B
C
D
Ans . A
Q. There are two straight lines in the x-y plane with equations:
ax + by = c
dx + ey = f
Do the two straight lines intersect?
I. a, b, c, d, e and f are distinct real numbers.
II. c and f are non-zero.
A
B
C
D
Ans . D
Q. 'O' is the centre of two concentric circles, AE is a chord of the outer circle and it intersects the inner
circle at points 'B' and 'D'. 'C' is a point on the chord in between 'B' and 'D'’.
What is the value of AC/CE?
I. BC/CD = 1
II. A third circle intersects the inner circle at 'B' and 'D' and the point 'C' is on the line joining the
centres of the third circle and the inner circle.
A
B
C
D
Ans . B
Q. Ghosh Babu has decided to take a non-stop flight from Mumbai to No-man’s-land in South America,
He is scheduled to leave Mumbai at 5 a.m., IST on December 10, 2000. What is the local time at
No-man’s-land when he reaches there?
I. The average speed of the plane is 700 km/hr.
II. The flight distance is 10,500 km.
A
B
C
D
Ans . D
Q. What are the ages of two individuals, X and Y?
I. The age difference between them is 6 years.
II. The product of their ages is divisible by 6.
A
B
C
D
Ans . D