-
Chapter 18: MISCELLANEOUS PART 2
TYPES OF MARKET STRUCTURES
Perfect Competition
- Participants are high both buyers and sellers.
- Products have many substitutes and no marketing or selling cost is incurred.
- Knowledge of participants for entering into market is perfect.
- Seller is Price taker not Price maker.
- Buyer willing to buy all at a certain price but none at price higher. So he is price maker.
Monopoly
- Buyers are many but seller is one.
- Product has no substitute or no close substitute
- Other competitors cant enter in market due to laws or patents.
- Price discrimination is seen between poor and rich. Seller is Price maker.
- Relative Price inelastic increase means demand decreases by less than X% for X% increase in price.
Natural monopoly is when there is extremely high fixed cost of distribution e.g. gas, water, electricity.
Monopolistic competition
- Many buyers and sellers but each selling its differentiated version of good.
- Marketing selling cost is high. Goods are of different brands where brand loyalty is seen till a limit but many substitutes are available.
- Unrestricted and free entry.
- Seller is Price maker to a level.
- Price increases by x% but demand decreases by less than x% - relatively inelastic. But more elastic than monopoly.
Oligopoly
- Buyers many but sellers few with intense competition.
- Product has close substitute and intense competition amongst sellers. If one sellers introduces change others have to follow. High cost of marketing and selling.
- Entry of new sellers tough due to economies of scale.
- Seller is price maker.
Monopsony
- Monopoly of the buyer but multiple sellers present.
- Entry closed for other buyers
- Seen where government wants to make a defense related purchase and multiple sellers are bidding for it.
- Buyer is price maker.
Economic Cost
Economic cost is the summation of explicit cost , implicit cost and normal profit. Explicit cost is needed for hiring or purchasing, implicit cost is incurred from own land or capital and normal profit is seen in monopolistic competition / perfect competition whereas abnormal profit is seen in monopsony, monopoly and oligopoly.
Economic cost is accounting cost plus opportunity cost.
Example is if a boy attends college then the accounting cost is calculated as a sum of tuition fee, travelling, cost of books, exam fee. But opportunity cost is the salary he could have earned if he had worked. Hence if his accounting cost is Rs. 1 lakh and opportunity cost is Rs. 2 lakh then the economic cost of attending college for him is Rs. 3 lakh.
Social Cost
Social cost is economic cost plus external cost. External cost is externalities like damage to environment done by the venture.
Total cost is sum of total fixed costs and total variable costs. Fixed costs are taxes, rents, license fee, depreciation. Variable costs are salary of casual workers, raw materials etc.
The total cost and total variable cost are parallel lines.
The total fixed cost is a straight line but the average fixed cost depends on the outputs and more the outputs more it will decline. Its shape is a Rectangular hyperbola.
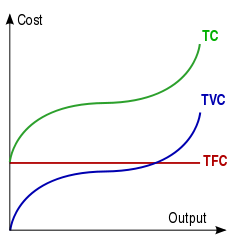
Fig 1: Total cost curve
Basic terms of Microeconomics
Want / Desire - Primary wants are food, shelter, clothing and secondary wants are comfort and luxury.
Consumption - Using goods and services to satisfy wants.
Utility - Satisfying power of a good or service. Marginal utility is the maximum price a consumer is willing to pay.
Production - Making goods or services that have utility. Marginal price of production is minimum profit a producer expects.
Demand - Willingness to buy a good at a certain price at a certain time.
Quiz
Score more than 80% marks and move ahead else stay back and read again!