-
Chapter 1: ENVIRONMENT
Introduction
Ecology is a subject which studies organisms and their interactions with themselves and with their physical environment.
Ecosystem is a functional unit of nature where the living organisms interact with each other and also with surrounding environment.
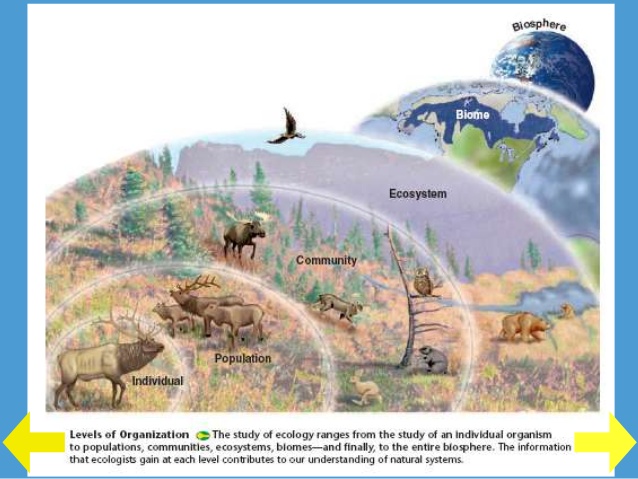
Fig 1: Biosphere to Individual
India
is among the 12 mega biodiversity countries in the world.
Of all the species in the world 70% are animals and rest
are plants.
In
animals 70% are insects. 8 percent of all species live
in India.
In
general, species diversity decreases as we move from
equator towards the poles.
The tropics have remained relatively undisturbed unlike the temperate regions that have seen glaciations. Tropical environments are less seasonal and more stable. Constant environments promote niche specialization and species diversity. However 40% of forest area has been lost in tropics compared to 1% in temperate areas.
In the North India there is a vast expanse of terrain consisting of sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. The peninsular plateau in south is made of igneous and metamorphic rocks.
47000 plant species are present in India. The country is 10th in World and 4th in Asia in terms of biodiversity. There are 15000 flowering plants that account for 6% of the worlds. 1200 bird species constituting 13% of worlds total and 2500 fish species constituting 12% of world’s fishes are present in India. Biodiversity decreases with increase in altitude.
Biodiversity
Hotspots or mega diversity reserves are place for
in-situ conservation of most threatened
reservoirs of bio diversity on earth. The criteria for a hotspot as said by Prof. Norman Myers are:
- The area should support >1500 endemic species
- It must have lost over 70% of its original habitat.
The variations in temperature of the place along with the variations in the precipitation have created biomes on earth viz. Deserts, grasslands, tropical, temperate, coniferous forests and arctic and tundra regions. Regional and local variations in the biomes have created many habitats.
A large ecosystem with its own distinct type of vegetation and animal life is called biome.
Niche means sum of activities and relationships of a species by which it uses all resources in its habitat for survival and reproduction. No two species can have the same niche.
Ecotone is a zone of junction between two or more ecosystems. E.g. Mangroves are zone between marine and terrestrial ecosystems.
Habitats
of organisms comprise of biotic and abiotic
components like temperature, water, light and soil.
Organisms and Environment
Eurythermal organisms tolerate vast range of temperatures and Stenothermal tolerate a narrow range of temperature.
Aquatic
animals face problem due to pH and salt concentration of
water. Fresh water organisms can’t live in salt water and
vice versa due to osmotic pressure. Euryhaline can
tolerate vast range of salinity and stenohaline cant.
40% of all known fish species are found in the freshwater ecosystem.
Light too is an important component as it is needed in photosynthesis. The animals to need it as they determine their foraging, migratory, reproductive activities based on the photoperiod.
Soil
too is important as the composition, grain size and
aggregation determines the grain size and this decides the
water retention capacity. Various types of vegetation are
possible based on this and this in turn supports a
different section of wildlife.
Responses to Abiotic factors:
Mammals,
birds, a few vertebrates and invertebrates are capable of
regulation both Thermo - regulation and
Osmo - regulation.
They
sweat during summer due to excess heat to cool the body.
In winter they shiver to generate heat. No plants and
99% of animals can’t regulate and hence are called
conformers.
Since body heat loss or gain is proportional to their surface area the small animals lose heat fast as their body area is less compared to their volume. Hence more energy will be lost in regulating. Thus they prefer conformation.
These animals prefer to migrate or go into hibernation during unfavorable conditions.
Adaptation: an attribute of an organism that enables it to survive and reproduce in the habitat.
E.g.:
kangaroo rats in North America meet their water
requirements by internal fat oxidation. Desert plants use
CAM pathway for photosynthesis. Mammals in colder areas
have shorter ears and limbs. Polar mammals have a thick
layer of fat below their skin to act as insulator.
Nature of interaction between species:
1. Predation: here the predator is the one who benefits and the prey loses.
2. Competition: multiple species compete for the same resource.
3. Parasitism: the parasite is benefited but the host is affected adversely.
4. Commensalism: the host isn’t benefited or harmed but the other species derives benefit
5. Mutualism: both the associating species benefit
6. Amensalism: one species is harmed but the other is unaffected.
7. Neutralism: species which interact but don’t affect each other in any way. It is very rare or nonexistent.
Energy and Environment
Sun
is the only form of energy for the entire biosphere. Of
the total solar energy incident on the earth only 50%
is photo-synthetically active. Out of this 2% is
used by the plants and this sustains all life.
Green
plants are the producers, the herbivore animals consume
them and the carnivores consume the herbivores. Thus
energy moves from one trophic level to the next.
After the death of the carnivores decomposers convert
their body into humus which is again used by the plants.
Thus energy flow is circular.
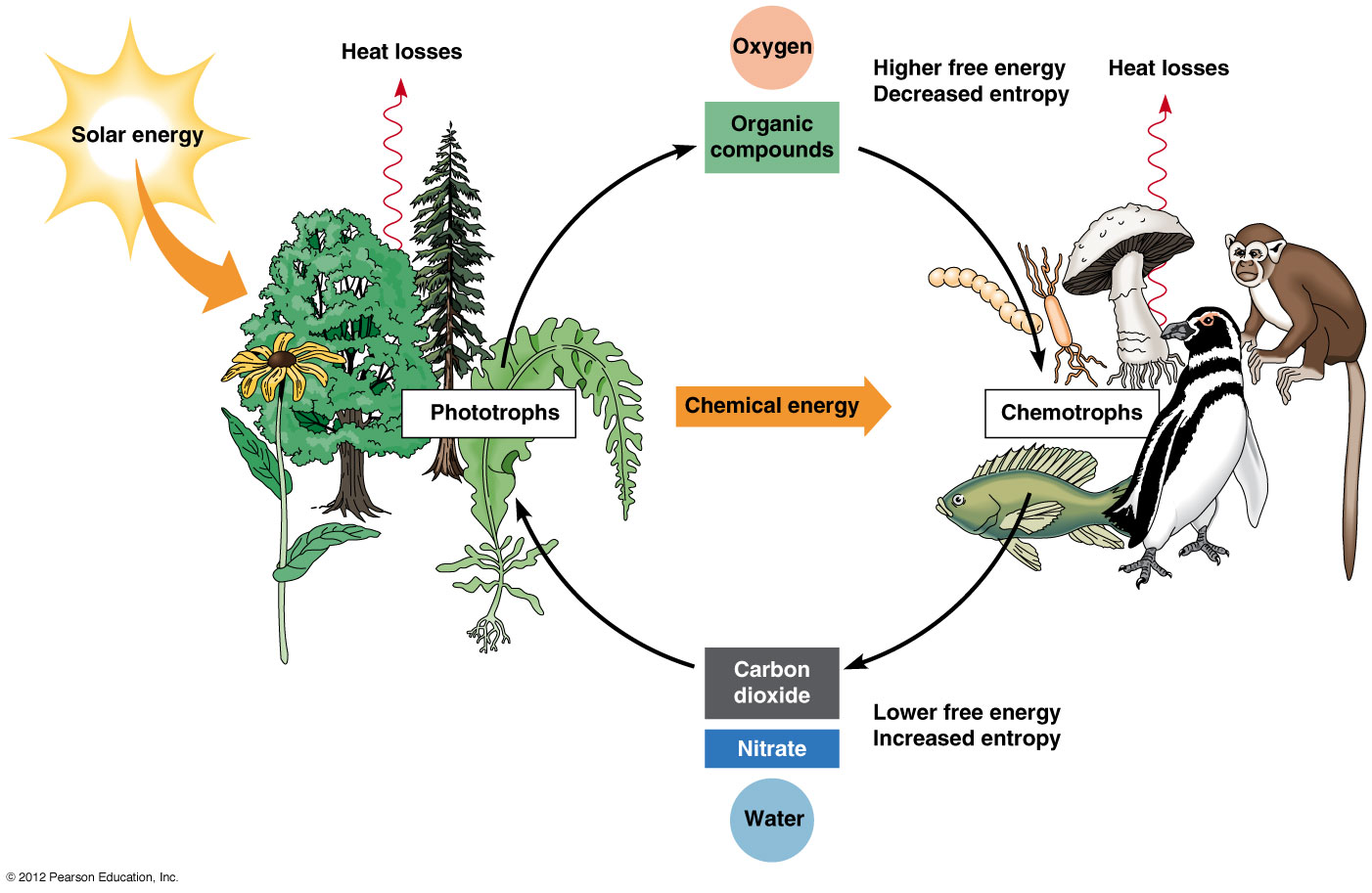
Fig 1: Circular flow
of energy
The energy that flows from one trophic level to the next is 10% of its total. The biomass at each level is calculated from the dry weight of the organism at the level, it too goes on decreasing for each trophic level. Hence both the energy and biomass structures are pyramidal. This isn’t seen at the aquatic biomass pyramid where a small standing crop of phytoplankton supports a larger mass of zooplankton.
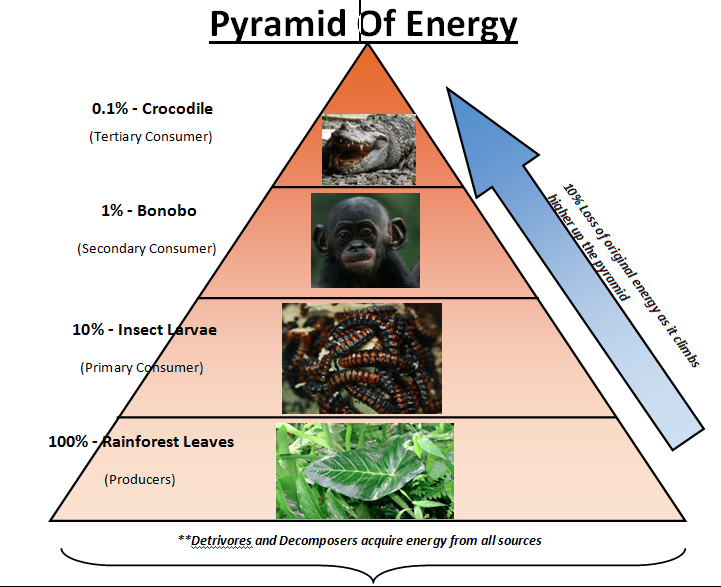
Fig 2: Energy pyramid of terrestrial systems
Biodiversity
in marine ecosystem is higher than the terrestrial
ecosystem. Insects and vascular plants are
completely absent here.
Maximum diversity in marine organisms is seen in the tidal zone near the shore.
Estuary
is a place where a river or lake opens into the sea. It is
partially enclosed area at the mouth of the river where
fresh water and salty sea water mix. Plants and animals in
estuary have adapted themselves to variations in salinity.
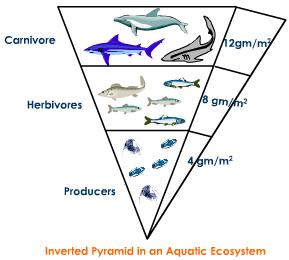
Fig 3: Inverted pyramid of marine systems
Conservation:
1. In situ: threatened plants and animals are preserved in their natural habitats by declaring these as protected areas. E.g.: national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, biosphere reserves.
2. Ex-situ: threatened animals and plants are taken out of their habitats and placed outside their natural setting in a place where they can be protected and cared. E.g.: zoological parks, cryo-preservation, botanical gardens, gene banks, conservation at molecular level.
Ecological succession:
Process by which communities of plants and animals species in an area are changed or replaced into another over a period of time is known as ecological succession.
Succession can be:
- Primary: this takes place on bare or unoccupied surface. The plant or animal species that invades this area are called pioneer species. This species show a high growth rate but a short life span.
- Secondary: this is the community that is formed after the community that occupied the region is removed or destroyed due to natural or human related events.
Solved Question Papers
Q. Consider the following pairs :
Terms sometimes seen in the news and Their origin
1. Annex—I Countries - Cartagena Protocol
2. Certified Emissions Reductions - Nagoya Protocol
3. Clean Development Mechanism - Kyoto Protocol
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?(UPSC CSAT 2016)
1 and 2 only
2 and 3 only
3 only
1, 2 and 3
Ans . C
All are associated with kyoto protocol
Q.With reference to an initiative called ‘The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity (TEEB)’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. It is an initiative hosted by UNEP, IMF and World Economic Forum.
2. It is a global initiative that focuses on drawing attention to the economic benefits of biodiversity.
3. It presents an approach that can help decision-makers recognize, demonstrate and capture the value of ecosystems and biodiversity.
Select the correct answer using the code given below (UPSC CSAT 2016)
1 and 2 only
3 only
2 and 3 only
1, 2 and 3
Ans . C
TEEB was launched by Germany and EU (2007)
Q.Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Proper design and effective implementation of UN-REDD+ Programme can significantly contribute to
1. protection of biodiversity
2. resilience of forest ecosystems
3. poverty reduction
Select the correct answer using the code given below. (UPSC CSAT 2016)
1 and 2 only
3 only
2 and 3 only
1, 2 and 3
Ans . D
Under REDD+ Developing country will have to prove the ‘result’ they have fought deforestation without harming local communities or biological diversity.
REDD+ also incorporates livelihood improvement
Q.What is ‘Greenhouse Gas Protocol’? (UPSC CSAT 2016)
It is an international accounting tool for government and business leaders to understand, quantify and manage greenhouse gas emissions
It is an initiative of the United Nations to offer financial incentives to developing countries to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and to adopt eco-friendly technologies
It is an inter-governmental agreement ratified by all the member countries of the United Nations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to specified levels by the year 2022
It is one of the multilateral REDD+ initiatives hosted by the World Bank
Ans . A
Q.With reference to ‘Agenda 21’, sometimes seen in the news, consider the following statements :
1. It is a global action plan for sustainable development
2. It originated in the World Summit on Sustainable Development held in Johannesburg in 2002.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (UPSC CSAT 2016)
1 only
2 only
Both 1 and 2
Neither 1 nor 2
Ans . A
Agenda 21 is a non-binding, voluntarily implemented action plan of the United Nations with regards to sustainable development. It is a product of the Earth Summit held in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, in 1992.
Q. Consider the following statements:
(1) The International Solar Alliance was launched at the United Nations Climate Change Conference in 2015.
(2) The Alliance includes all the member countries of the United Nations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?(UPSC CSAT 2016)
1 only
2 only
Both 1 and 2
Neither 1 nor 2
Ans . A
it includes only the 121 countries between Capricorn and Cancer receiving sunlight for 300 days or more
Q.With reference to the Agreement at the UNFCCC Meeting in Paris in 2015, which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. The Agreement was signed by all the member countries of the UN and it will go into effect in 2017.
2. The Agreement aims to limit the greenhouse gas emissions so that the rise in average global temperature by the end of this century does not exceed 2 °C or even 1.5 °C above pre-industrial levels.
3. Developed countries acknowledged their historical responsibility in global warming and committed to donate $ 1000 billion a year from 2020 to help developing countries to cope with climate change.
Select the correct answer using the code given below. (UPSC CSAT 2016)
1 and 3 only
2 only
2 and 3 only
1, 2 and 3
Ans . B
Paris Summit- not all nations have signed the agreement and there is no deadline to ratify it. Developed countries committed to give $100 billion by 2020.
Q.Consider the following statements:
1. The Sustainable Development Goals were first proposed in 1972 by a global think tank called the ‘Club of Rome’.
2. The Sustainable Development Goals have to be achieved by 2030.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?(UPSC CSAT 2016)
1 only
2 only
Both 1 and 2
Neither 1 nor 2
Ans . B
Q.The term ‘Intended Nationally Determined Contributions’ is sometimes seen in the news in the context of (UPSC CSAT 2016)
pledges made by the European countries to rehabilitate refugees from the war-affected Middle East
plan of action outlined by the countries of the world to combat climate change
capital contributed by the member countries in the establishment of Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
plan of action outlined by the countries of the world regarding Sustainable Development Goals
Ans . B
Q.What is/are the importance/importance of the ‘United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification’?
1. It aims to promote effective action through innovative national programs and supportive inter-national partnerships.
2. It has a special/particular focus on South Asia and North Africa regions, and its Secretariat facilitates the allocation of major portion of financial resources to these regions.
3. It is committed to bottom-up approach, encouraging the participation of local people in combating the desertification.
Select the correct answer using the code given below. (UPSC CSAT 2016)
1 only
2 and 3 only
1 and 3 only
1, 2 and 3
Ans . C
The implementation of the UNCCD is geared around five regional implementation annexes: Annex 1 for Africa, Annex 2 for Asia, Annex 3 for Latin America and the Caribbean, Annex 4 for Northern Mediterranean and Annex 5 for Central and Eastern Europe.
Q.Which one of the following is the best description of the term "ecosystem"? (UPSC CSAT 2015)
A community of organisms interacting with one another
That part of the Earth which is inhabited by living organisms
A community of organisms together with the environment in which they live.
The flora and fauna of a geographical area.
Ans . C
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the non-living components of their environment, interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic components are regarded as linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows.
Q. Which one of the following is the best description of the term “ecosystem”?(UPSC CSAT 2015)
A community of organisms interacting with one another
That part of the Earth which is inhabited by living organisms
A community of organisms together with the environment in which they live.
The flora and fauna of a geographical area.
Ans . C
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the non-living components of their environment, interacting as a system.
These biotic and abiotic components are regarded as linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows.
Q.Which one of the following is the process involved in photosynthesis? (UPSC CSAT 2014)
Potential energy is released to form free energy
Free energy is converted into potential energy and stored
Food is oxidized to release carbon dioxide and water
Oxygen is taken, and carbon dioxide and water vapour are given out
Ans . B
During photosynthesis, solar energy converted to chemical energy and stored in sugar molecule bonds. This chemical bond energy is potential (stored) energy.
Q.Which of the following adds/add carbon dioxide to the carbon cycle on the planet Earth?
Volcanic action
Respiration
Photosynthesis
Decay of organic matter
Select the correct answer using the code given below. (UPSC CSAT 2014)
1 and 3 only
2 only
1, 2 and 4 only
1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans . C
Volcanic action releases CO2 in the atmosphere.
Global carbon cycle involves a complex interplay of geological processes such as volcanic activity
Quiz
Score more than 80% marks and move ahead else stay back and read again!