-
Chapter 6: AGRICULTURE
Introduction
Agriculture is the main source of livelihood for 55% of the population. The food grain production of 2014-15 is at 252 million tones slightly less than previous year due to the drought. The schemes launched by the Dept. of Agriculture and Cooperation & Farmers Welfare are:
Ministry of Agriculture
Krishnnonati Yojana [ Umbrella Scheme]:
National food security mission [2007-8] launched to increase production of rice, wheat, pulses by 10, 8, 2 million tons resp. The mission is being continued into the 12th plan with a target of 10, 8, 4 for rice, wheat, pulses and 3 million tons increase in coarse cereals. Currently the program is being implemented with a share ratio of 50:50 between center and states in 623 districts of 28 states.
National food security mission – commercial crops: To enhance the productivity of cotton, jute and sugarcane. Thrust is on transfer of technology and share ratio is 50:50.
Mission for integrated development of horticulture: emphasis is on improving productivity, reduce post harvest losses, and improve quality of seeds and planting material. The current production of horticulture products is at 283 million tons [2014-15]
National mission on oilseeds and oil palm: target is to increase production of vegetable oils from oil seeds, oil palm to 9.5 million tons by end of 12th plan. Strategy is increase seed replacement ratio, increase quality planting material, irrigation coverage, inter cropping with others and use of fallow and wastelands for cropping.
National mission for sustainable agriculture: emphasis is to make agriculture more remunerative, sustainable, climate resilient and remunerative.
Soil health card scheme:
To be distributed to farmer’s at interval of three years so that they can test their fields and appropriately put fertilizers to their farms. 12 indicators shall be tested in every soil sample.
Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana:
Organic farming promotion scheme. Cluster of farmers shall be formed and motivated to do organic farming. 10000 clusters covering 5 lac acres are targeted. Certification and end to end marketing of produce shall be done.
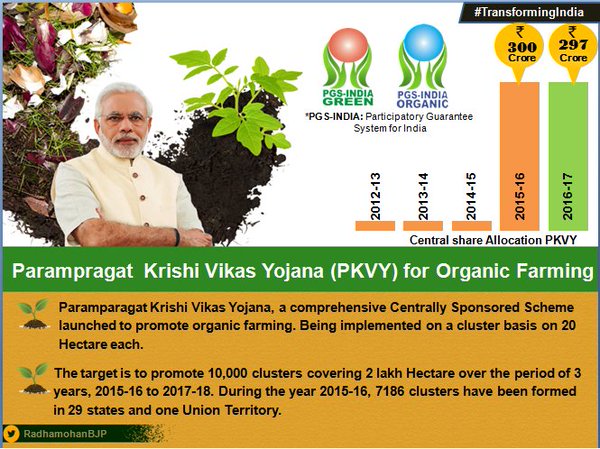
Fig 1: Organic farming
Mass media support to agriculture extension and focused publicity campaign:
1. Agro clinic and agro business centers: provides service and support to farmers for setting up of self employment ventures.
2. Information dissemination through agriculture fairs.
3. National e-governance plan in agriculture: timely providing information to farmers using I.C.T
4. Kisan call centers: provide toll free information to farmers
5. Farmers portal: to access all information on agricultural activities using a graphical interface
6. M - kisan portal: to send S.M.S, I.V.R.S and U.S.S.D service to farmers by Agro - Scientists.
7. DD Kisan: fully dedicated channel for farmers.
8. National Agro - tech infra fund: to be used to promote a national market by creating an e-platform to be deployed on all state and UT's wholesale markets.
9. Price stabilization fund: to purchase Agro - horticulture products and reduce price fluctuations and protect farmers and consumers.
PM krishi sinchai Yojana:
Providing access to water for
every farm by ensuring end to end irrigation supply chain
by building distributing networks, farm gate applications.
Micro irrigation and its benefits
Micro irrigation has a coverage potential of 69 million hectares and currently only 13% area of that is being covered. The micro irrigation systems provide a water savings of up to 40% over conventional flood irrigation systems and lead to crop productivity increase. The latter is due to water application directly at the root zone. The piped system of transporting water from dams to fields can save water loss by 70% and make the entire system water efficient by 90%.
The Marathwada region of Maharashtra which grows sugarcane consumes 2000 liters of water for a kilogram of sugar and so bringing a hectare of sugarcane under micro irrigation can save enough water to bring 5 hectares of cotton under cultivation. Installation of micro irrigation systems can cost Rs. 75000 per hectare but the price can lead to huge savings too.
PM Krishi Sinchayi Yojana

Fig 2: PMKSY
National crop insurance programs:
Provide financial support and stabilize farm income during adverse conditions when crops fail due to pests, disease, weather or natural calamities.
Research and Development Institutes
Indian council of agriculture research [I.C.A.R]: Under the Dept. Of Agriculture Research, Ministry of Agriculture. It has one of the world’s largest network of institutes and is mandated with coordinating, managing R&D in agriculture. New schemes launched by it are farmer FIRST [farmer, innovation, research, science and technology], student READY [rural entrepreneurship and awareness development Yojana], and A.R.Y.A [attracting and retaining youth in agriculture].
Department of Animal Husbandry, Dairying & Fisheries:
Department of animal husbandry, dairying, fisheries: is another department under ministry of agriculture. It conducts livestock census every five years [1st in 1919]. India is the world’s leading producer of milk and the per capita availability is higher than the world. The department looks after promotion of dairy activities in non operation flood areas while the national dairy development board looks after operation flood areas. Schemes launched by it are:
National program for bovine breeding and dairy development: N.P.B.B & D.D
Focused on increasing artificial insemination by its network of M.A.I.T.R.I [Multipurpose Artificial Insemination Technician in Rural India] and N.P.D.D focused on creating the infrastructure for procurement, processing, marketing of milk and milk products.
Fisheries Sector
Fishery is a highly growing sector where India ranks second in world with 5.6% of global fish production. It is also second after china in aquaculture. The total output of fish is 10 million tons with 6.5 from inland and rest from marine. India has about 2200 species of fish i.e. 11% of global fish species. 65% of Indian fishes live in the sea, 3.3% in cold freshwater, 25% in warm freshwater and rest in estuaries. Ongoing schemes were brought under Blue Revolution – an umbrella referring to integrated and holistic development of fisheries and aquaculture.
Solved Question Papers
Q.Consider the following statements :
The nation-wide ‘Soil Health Card Scheme’ aims at
1. expanding the cultivable area under irrigation.
2. enabling the banks to assess the quantum of loans to be granted to farmers on the basis of soil quality.
3. checking the overuse of fertilizers in farmlands.
Which of the above statements is/are correct? (UPSC CSAT 2017)
1 and 2 only
3 only
2 and 3 only
1, 2 and 3
Ans . B
A soil health card provides information about 12 soil parameters, so farmer can use appropriate fertilizers.
Q. What is/are the advantage/advantages of implementing the ‘National Agriculture Market’ (NAM) scheme?
1. It is a pan-India electronic trading portal for agricultural commodities.
2. It provides the farmers access to nationwide market, with prices commensurate with the quality of their produce.
Select the correct answer using the code given below :(UPSC CSAT 2017)
1 only
2 only
Both 1 and 2
Neither 1 nor 2
Ans . C
Q. Which of the following practices can help in water conservation in agriculture?
1. Reduced or zero tillage of the land
2. Applying gypsum before irrigating the field
3. Allowing crop residue to remain in the field
Select the correct answer using the code given below : (UPSC CSAT 2017)
1 and 2 only
3 only
1 and 3 only
1, 2 and 3
Ans . D
Crop residues or other organic matter left in or added to the field improve water penetration and moisture retention
Gypsum application can solve the water percolation process.
zero tillage faming helps in moisture conservation.
Q.What is the application of Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT) Technology? (UPSC CSAT 2017)
Production of biolarvicides
Manufacture of biodegradable plastics
Reproductive cloning of animals
Production of organisms free of disease
Ans . C
SCNT technology was used for cloning the sheep “Dolly
Q.With reference to agriculture in India, how can the technique of ‘genome sequencing’, often seen in the news, be used in the immediate future?
1. Genome sequencing can be used to identify genetic markers for disease resistance and drought tolerance in various crop plants.
2. This technique helps in reducing the time required to develop new varieties of crop plants.
3. It can be used to decipher the host-pathogen relationships in crops.
Select the correct answer using the code given below: (UPSC CSAT 2017)
1 only
2 and 3 only
1 and 3 only
1, 2 and 3
Ans . D
Benefits of human genome sequencing that – “It is the sequence of bases in DNA that determines the genetic information of a given organism. So, learning about the DNA sequences can lead to an understanding of their natural capabilities that can be applied toward solving challenges in health care, agriculture, energy production, environmental remediation.”
Q.Which one of the following best describes the main objective of ‘Seed Village Concept'? (UPSC CSAT 2015)
Encouraging the farmers to use their own farm seeds and discouraging them to buy the seeds from others
Involving the farmers for training in quality seed production and thereby to make available quality seeds to others at appropriate time and affordable cost
Earmarking some villages exclusively for the production of certified seeds
dentifying the entrepreneurs in village and providing them technology and finance to set up seed companies
Ans . B
A village, wherein trained group of fanners are involved (generally in a self-help group) in production of seeds of various crops and cater to the needs of themselves, fellow fanners of the village and fanners of neighboring villages in appropriate time and at affordable cost is called “a seed village”.
Q.What can be the impact of excessive/inappropriate use of nitrogenous fertilizers in agriculture?
1. Proliferation of nitrogen-fixing microorganisms in soil can occur.
2. Increase in the acidity of soil can take place
3. Leaching of nitrate to the ground-water can occur.
Select the correct answer using the code given below. (UPSC CSAT 2015)
1 and 3 only
2 only
2 and 3 only
1, 2 and 3
Ans . C
Increasing the amount of nitrogen based fertilizer does not lead to more micro-organisms in the field. If it did, just one dose of fertilizer would make a farm nitrogen rich for years together.
Excessive use of nitrogen fertilizers resulting in soil acidity
Nitrogen fertilizers break down into nitrates and travel easily through the soil. Because it is water-soluble and can remain in groundwater for decades, the addition of more nitrogen over the years has an accumulative effect.
Chapter Review
Score more than 80% marks and move ahead else stay back and read again!