-
Chapter 2: INDUSTRIAL LOCATION FACTORS - COTTON, TEXTILE INDUSTRY
Introduction
Cotton is a non perishable raw material with no weight loss when converted to yarn or textile and so proximity to source of raw materials doesn't bring any benefit. The factors that determine the location of cotton industry are labor, proximity to markets, energy supply and availability of capital or finance. Climate to is a factor as dry climate not suitable for mass production as cotton threads break and manually have to be joined again.Textile Industry in Mumbai and Japan
Similar factors led to the development of textile industry in Mumbai and Japan. Both regions had black cotton soil needed for manufacturing short, medium staple cotton. Port location in both these areas made import of cotton staple and export of finished textiles suitable. The presence of skilled labor in Mumbai and connectivity via road, rail and sea was present. Energy needs were met and water too was present for dyeing and bleaching. Population in Mumbai was high so market for the textiles existed. The capital needed for investment was obtained by huge profits earned during American Civil War.Osaka in Japan too was a port location with humid climate. Labor was skilled but not abundant and so mechanization was high. River water was used for dyeing and bleaching. Energy needs were met and since indigenous demand was less textiles could be exported to other locations.
Rise and fall of British Textiles
Industrial revolution enabled Britain to get a dominant position in the textile trade. It imported raw cotton from India and sold finished products to colonies. Humid climate in Britain and presence of Liverpool and Manchester port made textile manufacturing possible. Mechanization reduced demand for labor. Energy needs were met initially from water and then coal. Soft water for dyeing and bleaching was also obtained from rivers.
However dependence on foreign colonies for raw materials cost it. After the World Wars the dominant position in the colonies was gone and market was no longer available. Cheaper textiles were obtained from other Asian colonies and Britain textiles industry no longer got larger orders. The Business moved towards more profitable businesses like light engineering, ship building and heavy chemicals.
The textile industry of Britain soon faded away.
American Textiles Industry
USA has two major regions for textile industry: New England belt in the North East and Southern Belt. In New England proximity to New York and Boston meant that domestic demand as well as export could be done. The immigrants to New York were used as cheap labor. However due to mountainous regions the factories couldn't be expanded. Today it serves as a center for high end specialized fashion products.
The Southern belt however covered a vast area. It used slave labor but later moved to mechanization. Today the paper mills could be used to manufacture rayon from pulp so even synthetic industry developed. This regions manufacturers textiles for consumption of the masses.
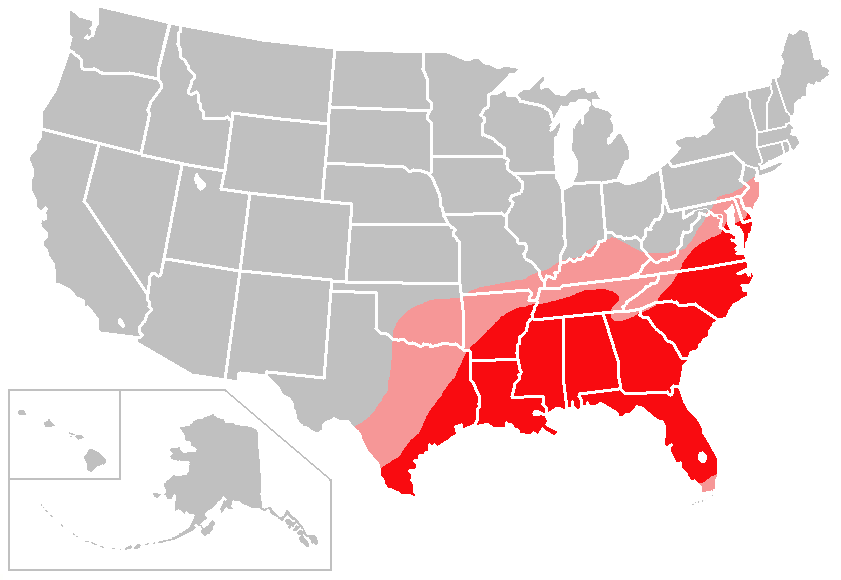
Fig 1: Cotton belt in USA.
Silk Industry and Development
Silk development or sericulture needs cheap and abundant labor. China and Japan during the medieval times had poor peasants who could use silk production as a secondary income source. The European nations too saw silk production but it didn't succeed except in Lyon, France. The European peasantry wasn't able or interested in the pain staking work. France saw an epidemic that wiped out the silkworms and the silk industry never recovered. However Lyon is known for silk garments even though there is no local production. This is due to presence of fashion designers and skilled labor in France. Natural silk was non bulky, non perishable and easy to import from China. The high demand for silk accessories also meant that market was available.
America too failed in the silk experiment as its farmers found more profit in other crops.
Japan was a major producer of silk but today accounts for less than 0.5% of production. This is because:
- Labor in Japan moved towards more productive occupations like industry.
- Demand declined as silk garments were now replaced by other clothes. The silk kimono is now worn in festivals but this low demand can be met by imported silk.
- As demand declined land, capital and labor from silk industries moved towards automobile industry e.g. Toyota.
Currently China is responsible for 80% of Silk production and India is responsible for 18%.
Factors for Chinese domination:
- China is a leader in univoltine, bivoltine and polyvoltine silk varieties. The availability of cheap, abundant labor is favorable factor.
- Government policy allows formation of Silk Communes which have standard procedure and better output than individual farmers. The training and extension services too are provided.
- Scientists had developed silkworm that could rear 7 times a year. The proximity to Shanghai port means that export is easier.
- Sericulture and fish farming is done together and waste from sericulture is given to fishes.
Factors for Growth in India:
India has high demand for silk garments like sarees but the supply is limited hence it has to import from China. The Southern states grow Mulberry silk and North and NE states grow non mulberry silk like Eri,Tasar, Muga. Mulberry tree can be grown in any soil and weather condition. Labor need not be skilled and capital needs aren't high. Hence Silk production is suitable for India.
- Karnataka is leading in silk production due to climate being favorable to Mulberry plantation. The hybrid silk worms used rears 6 times a year. The labor is also available. Japanese agency is providing technical cooperation.
- Kanchipuram has a good silk industry due to generation of silk weavers so traditional skill. Supply is from Karnataka and good demand for sarees are there in India.
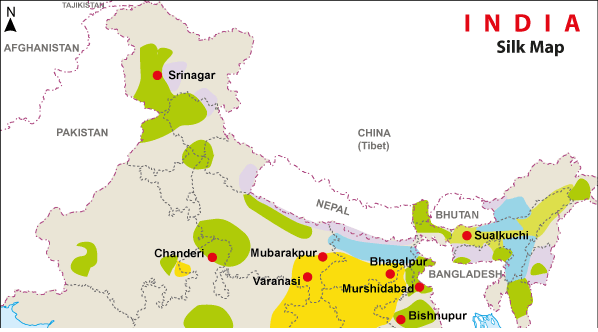
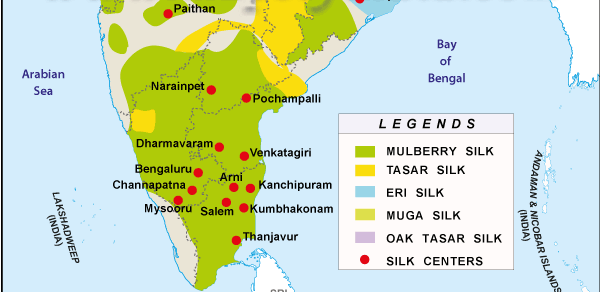
Fig 1: Silk map of India
SILK TEXTILE
Silk textile was essentially a household industry in the early stage of its development. The Mughals were very much fond of silk clothes. The cotton goods used to be exported to the countries of south-west Asia and Europe. The first silk mill was, however, located at Haora by the East Indlia Company in 1832. The industry made tremendous progress after Independence.
The state of Karnataka is the largest producer of silk textile.
India is one of the important exporters of silk textile. Silk and silk products are exported to USA, UK, Kuwait, Russia, Oman, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, and UAE.
Questions for UPSC Mains
Factors for the growth of cotton in mumbai, manchester
Rise of China as the world's silk capital?