-
Chapter 11: WEATHER PHENOMENON
Introduction
Weather v. Climate
- Weather changes frequently but Climate is the average atmospheric conditions of an area over a considerable time.
- Climate of temperate latitudes is far more variable than the tropics.
Points to remember about the Weather effect's
- Death rates of tropics are higher than deserts as germs find it difficult to transmit easily in dry conditions compared to humid conditions.
- Rainfall, snow, sleet, hail are types of precipitation and are measured by Rain gauge.
- Places with the same mean annual rainfall are joined by the lines called “Isohyet”.
- Mercury is used in the Barometer as it is the heaviest known liquid. The mercury column at sea level is 30 inches approx. or 1013 milli-bar / 760 mm of Hg [Mercury].
- Lines called isobars join regions of high pressure.
- The Temperate latitudes see higher variations in pressure which leads to cyclones and anti-cyclones. As one goes higher in altitude the pressure decreases. The drop is 1 inch for every 900 feet ascent in height.
- Aeroplanes use a modified barometer called Altimeter.
- Temperature decrease is 1 Fahrenheit drop for 300 feet ascent in altitude.
- Humidity is the measure of dampness in the atmosphere. It has two types:
- Absolute and Relative humidity. The Absolute humidity is the amount of water vapor in grams per cubic meter.
- Relative humidity is the amount of water vapor present in air at a particular temperature compared to the total amount of water vapor, air can hold at that temperature.
Relative humidity = 80%; This means Air holds 4/5th of the water vapor it can hold.
Important instruments related to Weather
- Wind director – Wind vane
- Wind speed – Anemometer
- Relative Humidity - Hygrometer
- Places with equal sunshine duration are joined by “Isohels”.
- “Isonephs” are lines that join places with equal degree of cloudiness.
Formation of thunderstorms:
Heavy rainfall with thunder and lightning. They usually last for short amount of time. Cumulonimbus clouds are formed. This leads to atmospheric instability and convectional rainfall.
1. Air motion is upwards.
2. The accumulation of water increases and water droplets descend the surrounding is cooled. This leads to more downward draft and spreads throughout the entire cumulonimbus.
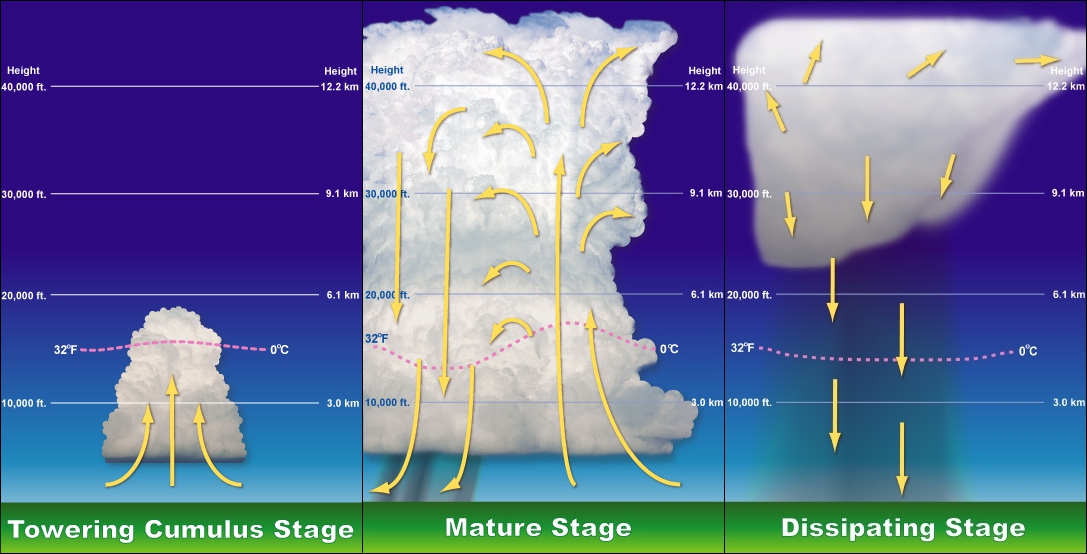
Fig 1:
Formation of thunderstorms
Types of thunderstorms:
1. Thermal thunderstorms – localized, intense heating of ground.
2. Orographic thunderstorms – obstruction due to mountains leads to it as forcible vertical movement is needed.
3. Cold front thunderstorms – hot and cold air collide to get this.
Tornadoes:
Occurs mostly in temperate regions where cold and warm air meets. South east of USA is called “Tornado Alley”.
Polar stratospheric clouds:
They are formed in winter and contain nitric acid, sulfuric acid and water. Nitric acid reacts with CFC to create chlorine. This creates a chlorine concentration in winter. This chlorine reacts with oxygen molecule of ozone and destroys the ozone layer.
Ozone depletion is more at southern pole and is called ozone hole - “Thinning of ozone layer in stratosphere below threshold” [not an actual hole].
El - Nino and La - Nina
There
are
oscillations in the pressure gradient and air circulation every
2-3 years in South Pacific Ocean. This is called El Nino
Southern Oscillation.
The term "El Niño" refers to "the boy" / "Child christ" , so named
because the pool of warm water in the annual weak warm ocean
current that ran southwards along the coast of Peru and Equador
around Christmas. "La Niña", the 'opposite' of El Niño,
translates to "the girl".
During a normal year the following events are seen:
- The south equatorial current takes warm water to Australia and creates a low pressure region. This heats the air and it rises upwards. The resultant atmospheric instability leads to rainfall in Australia.
- The air that rises up cools and diverges. It comes to the South American coast. Due to this high pressure is created and has a desiccating effect on the Atacama Desert.
- This is High pressure and low pressure formation is called Walker Cells.
- The south equatorial current takes warm water to the west from east. This causes up-welling at Peru coast and rich fisheries at Peru.
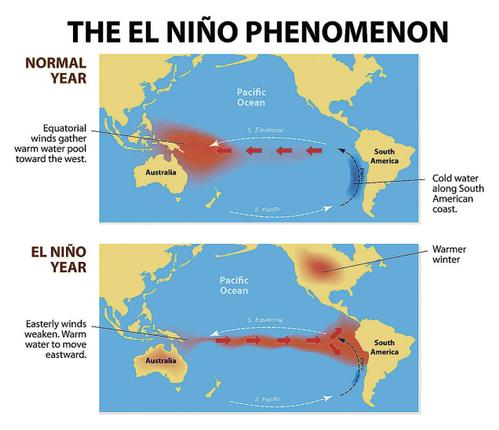
Fig 2: El nino
During El Nino year:
1. The south equatorial current weakens and water piling is reduced to Australia.
2. The abnormal cooling of Australian region and warming of Peruvian coast is seen. The low pressure condition over Peru and high pressure over Australia causes drought. Reversing of walker cells is observed.
3. This causes rainfall in Atacama Desert. The up-welling at Peru coast is affected and the fishery business goes down.
4. El Niño causes droughts in India and Indonesia as well.
During La Nina year:
1. Walker cells are intensified. This leads to higher rainfall in Australia and higher up-welling in Peru due to which fishes are more.
2. India too receives good rainfall.
Solved Question Papers
Q.In the South Atlantic and South Eastern Pacific regions in tropical latitudes, cyclone does not originate. What is the reason? (UPSC CSAT 2015)
Sea Surface temperature are low
Inter Tropical Convergence Zone seldom occurs
Coriolis force is too weak
Absence of land in those regions
Ans . A
Coriolis force is weak only in the region around 0-5 degrees North or South latitudes.
ITCZ formation is not essential to the formation of cyclones. Cyclones are formed in regions where ITCZ does not form, for e.g. in North Atlantic.
Absence of land boosts cyclones. Presence of land cuts off moisture from the cyclone.
For cyclone formation, a sea temperature of at least 26 degree Celsius is needed. In the South-eastern pacific and South Atlantic region cold currents are found. This leads to lower sea temperatures. Hence, cyclones don’t form there
Q.The seasonal reversal of winds is the typical characteristic of (UPSC CSAT 2014)
Equatorial climate
Mediterranean climate
Monsoon climate
All of the above climates
Ans . C
Monsoon connotes the climate associated with seasonal reversal in the direction of winds
Chapter Review
Score more than 80% marks and move ahead else stay back and read again!