HOW TO KICK-START CDS PREPARATION
Introduction
How to use upscfever.com for preparation
CDS syllabus includes:
| Subject |
|---|
| General Aptitude |
| History of India |
| Geography |
| Current events and Scientific facts |
Examination Scheme
Most of the services require degree from a recognized university. Below exam is for Army, Navy and Airforce academy. All questions are objective.
| Subject | Marks |
|---|---|
| English | 100 |
| General knowledge | 100 |
| Engineering mathematics | 100 |
| Total | 300 |
Exam for Officers training academy is also objective type.
| Subject | Marks |
|---|---|
| English | 100 |
| General knowledge | 100 |
| Total | 200 |
An interview is conducted for the successful candidates.
Promotional Avenues
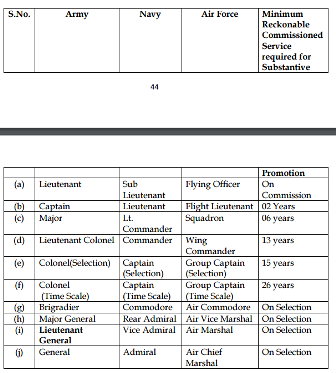 Fig 2: Promotional avenues
Fig 2: Promotional avenuesExamination Syllabus
STANDARD AND SYLLABUS OF THE EXAMINATION STANDARDThe standard of the papers in Elementary Mathematics will be of Matriculation level. The standard of papers in other subjects will approximately be such as may be expected of a graduate of an Indian University.
SYLLABUS ENGLISH (Code No. 01)
The question paper will be designed to test the candidates’ understanding of English and workmanlike use of words.
GENERAL KNOWLEDGE (Code No. 02)
General Knowledge including knowledge of current events and of such matters of everyday observation and experience in their scientific aspects as may be expected of an educated person who has not made a special study of any scientific subject. The paper will also include questions on History of India and Geography of a nature which candidate should be able to answer without special study.
ELEMENTARY MATHEMATICS (Code No. 03) ARITHMETIC
Number System—Natural numbers, Integers, Rational and Real numbers.
Fundamental operations, addition, substraction, multiplication, division, Square roots, Decimal fractions.
Unitary method, time and distance, time and work, percentages, applications to simple and compound interest, profit and loss, ratio and proportion, variation.
Elementary Number Theory—Division algorithm. Prime and composite numbers.
Tests of divisibility by 2, 3, 4, 5, 9 and 11. Multiples and factors. Factorisation Theorem.
H.C.F. and L.C.M. Euclidean algorithm.
Logarithms to base 10, laws of logarithms, use of logarithmic tables.
ALGEBRA
Basic Operations, simple factors, Remainder Theorem, H.C.F., L.C.M., Theory of polynomials, solutions of quadratic equations, relation between its roots and coefficients (Only real roots to be considered).
Simultaneous linear equations in two unknowns—analytical and graphical solutions.
Simultaneous linear inequations in two variables and their solutions.
Practical problems leading to two simultaneous linear equations or inequations in two variables or quadratic equations in one variable & their solutions.
Set language and set notation, Rational expressions and conditional identities, Laws of indices.
TRIGONOMETRY
Simple trigonometric identities.
Use of trigonometric tables.
Simple cases of heights and distances.
GEOMETRY
Lines and angles, Plane and plane figures, Theorems on (i) Properties of angles at a point,
(ii) Parallel lines,
(iii) Sides and angles of a triangle,
(iv) Congruency of triangles,
(v) Similar triangles,
(vi) Concurrence of medians and altitudes,
(vii) Properties of angles, sides and diagonals of a parallelogram, rectangle and square,
(viii) Circles and its properties including tangents and normals,
(ix) Loci.
MENSURATION
Areas of squares, rectangles, parallelograms, triangle and circle.
Areas of figures which can be split up into these figures (Field Book),
Surface area and volume of cuboids,
lateral surface and volume of right circular cones and cylinders,
surface area and volume of spheres.
STATISTICS
Collection and tabulation of statistical data,
Graphical representation frequency polygons, histograms, bar charts, pie charts etc.
Measures of central tendency.
INTELLIGENCE AND PERSONALITY TEST
The SSB procedure consists of two stage Selection process - stage I and stage II.
Only those candidates who clear the stage I are permitted to appear for stage II. The details are:-
(a) Stage I comprises of Officer Intelligence Rating (OIR) tests are Picture Perception* Description Test (PP&DT). The candidates will be shortlisted based on combination of performance in OIR Test and PP&DT.
(b) Stage II Comprises of Interview, Group Testing Officer Tasks, Psychology Tests and the Conference.
These tests are conducted over 4 days. The details of these tests are given on the website www.joinindianarmy.nic.in. The personality of a candidate is assessed by three different assessors viz.
The Interviewing Officer (IO),
Group Testing Officer (GTO)
Psychologist.
There are no separate weighage for each test. The mks are allotted by assessors only after taking into consideration the performance of the candidate holistically in all the test.
In addition, marks for Conference are also allotted based on the initial performance of the Candidate in the three techniques and decision of the Board.
All these have equal weightage.
The various tests of IO, GTO and Psych are designed to bring out the presence/absence of Officer Like Qualities and their trainability in a candidate.
Accordingly candidates are Recommended or Not Recommended at the SSB.