-
HOW TO KICK-START SSC - CGL PREPARATION
Introduction
Staff Selection Commission conducts recruitment to lower posts of Government of India via exams. Combined Graduate level examination is usually held once a year in February.
How to use upscfever.com for preparation
The questions of SSC exam are easier than the UPSC and so a studyplan of UPSC can also be adapted for SSC. The timing of the exam in february means the economic survey is not yet released for the year and so the previous one is used. The additional information of people appearing in news also has to be remembered. This is a feature SSC doesn't share with UPSC.
Staff selection commission has the following subjects for preparation:
| Subject |
Click below |
| General Aptitude | link |
| History | link |
| Geography | link |
| Environment | link |
| Science | link |
| Polity | link |
| Culture | link |
| Current affairs | India Yearbook and Economic survey |
| Economy | link |
| Aptitude | link |
Examination
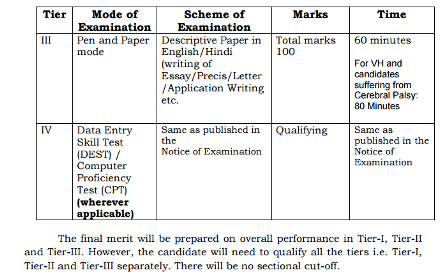
There are three to four tiers of examination and the candidate has to qualify in each level to be eligible for the next. Interviews shall not be conducted for these examinations. Selected candidates are recruited in Group B and Group C posts.
Introduction
SSC conducts recruitment for the non technical posts of
Group B and C in central government.
Examination
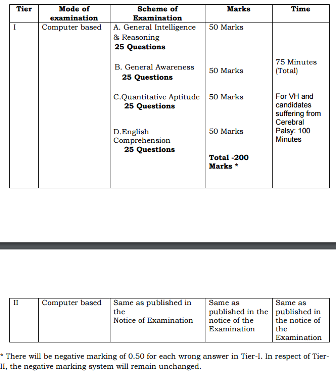
General Intelligence & Reasoning :It would include questions of both verbal and non-verbal type. This component may include questions on analogies, similarities and differences, spatial visualization, spatial orientation, problem solving, analysis, judgement, decision making, visual memory, discrimination, observation, relationship concepts, arithmetical reasoning and figural classification, arithmetic number series, non-verbal series, coding and decoding, statement conclusion, syllogistic reasoning etc.
B. General Awareness :
Questions in this component will be aimed at testing the candidates general awareness of the environment around him and its application to society. Questions will also be designed to test knowledge of current events and of such matters of every day observations and experience in their scientific aspect as may be expected of any educated person. The test will also include questions relating to India and its neighbouring countries especially pertaining to sports, History, Culture, Geography, Economic Scene, General Polity, Indian Constitution, scientific Research etc. These Questions will be such that they do not require a special study of any discipline.
C. Numerical Aptitude :
The questions will be designed to test the ability of appropriate use of numbers and number sense of the candidate. The scope of the test will be the computation of whole numbers, decimals and fractions and relationships between numbers.
It will test sense of order among numbers, ability to translate from one name to another, sense or order of magnitude, estimation or prediction of the outcome of computation, selection of an appropriate operation for the solution of real life problems and knowledge of alternative computation procedures to find answers. The questions would also be based on arithmetical concepts and relationship between numbers and not on complicated arithmetical computation (The standard of the questions will be of 10+2 level).
D. English Comprehension :
Candidates’ ability to understand correct English, his basic comprehension and writing ability, etc. would be tested. (The questions in the components A,B & D will be of a level commensurate with the Essential Qualification prescribed for the post viz; graduation).
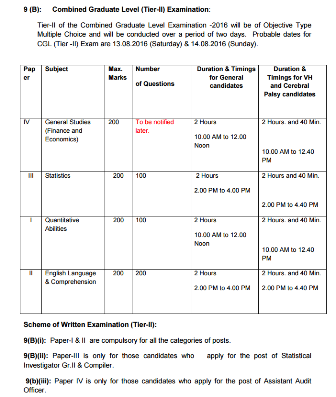
SYLLABUS TIER-II OF THE EXAMINATION :
Paper-I : Arithmetic Ability :
This paper will include questions on problems relating to Number Systems, Computation of Whole Numbers, Decimals and Fractions and relationship between Numbers, Fundamental Arithmetical Operations, Percentage, Ratio and Proportion, Average, Interest, Profit and Loss, Discount, Use of Table and Graphs, Mensuration, Time and Distance, Ratio and Time etc.
Paper-II :
English Language & Comprehension :Questions in this components will be designed to test the candidate’s understanding and knowledge of English Language and will be based on error recognition, fill in the blanks (using verbs, preposition, articles etc), Vocabulary, Spellings, Grammar, Sentence Structure, Synonyms, Antonyms, Sentence Completion, Phrases and Idiomatic use of Words, etc. There will be a question on passages and comprehension of passages also. (The standard of the questions will be of 10+2 level).
Paper-III : Commerce/Mathematics/Statistics/Economics for Investigator Grade-II, for Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation and Compiler for Registrar General of India, Ministry of Home Affairs.
A. STATISTICS
Probability, Probability Distributions, Binomial, Poisson, Normal, Exponential. Compilation, classification, tabulation of Statistical Data, Graphical presentation of data. Measures of central tendency, measures of dispersion, measures of association and contingency, scatter diagram, correlation coefficient, rank correlation coefficient and linear regression analysis ( for two or more variables ) excluding partial correlation coefficients. Concept of Population, random sample, parameters, statistics, sampling distribution of x properties of estimators and estimation of confidence intervals. Principles of sampling, simple random sampling, stratified sampling, systematic sampling etc., Sampling and non-sampling errors, type-I and type-II errors. Concepts of Hypothesis – Null and alternate, Testing of hypothesis for large samples as well as small samples including Chi-square tests ( Z, t, F, 2 tests ). Index Numbers, Time series analysis – components of variation and their estimation.
B. ECONOMICS GENERAL ECONOMICS
1. Demand and Supply Analysis, including Laws and Interaction of Demand and Supply. 2. Production Function and Laws of Returns. 3. Commodity Pricing – Characteristics of various Market Forms and Price Determination under such Market Forms. 4. Theory of Factor Pricing – Rent, Wage, Interest and Profit. 5. Theory of Employment – Classical and Neo-classical Approach.
6. Keynesian Theory of Employment – Principles of Effective Demand. Meaning and Importance of Investment, Relation between Saving and Investment, Multiplier Effect and the process of Income Generation, Post Keynesian Development. 7. Nature and Functions of Money, Value of Money, Fluctuations in the value of Money – Inflation and Deflation, Monetary Policy, Index Number. 8. International Trade-Free Trade and Protection, Theories of International Trade. 9. Foreign Exchange – Determination of the rate of Exchange – Purchasing Power Parity theory and Balance of Payment Theory. 10. Public Finance – Nature. Scope and importance of Public Finance. 11. Taxation – Meaning, Classification and Principles of Taxation, Incidence of Taxation. 12. Deficit Financing. 13. Fiscal Policy.
INDIAN ECONOMICS AND GENERAL STATISTICS
1. Statistical Investigation – Meaning and Planning of Investigation. 2. Collection of data and editing of data. 3. Types of sampling. 4. Schedule and questionnaire. 5. Presentation of data – classification, tabulation, etc. 6. Measures of Central Tendency. 7. National Income and Accounting – Estimation of National Income, Trends in National Income, Structural changes in the Indian Economy as seen in National Income Data.
8. Agricultural sector – Agricultural Development during Plan Period, Rural Credit, Agricultural Price Policy, Rural Development Co-operation and Panchayati Raj. 9. Industrial Policy and Industrial Development. 10. Problems of Economic Development – Indian Planning – Objectives, Techniques and its evolution, Five Year Plans and Role of National Development Council. 11. Profile of Human Resources – Population and Economic Development, Demographic Profile of India, Nature of Population Problem – Poverty, Inequality, Unemployment Problem, Labour Problem, Population Control and Government Policy. 12. New Economic Policy and Welfare Schemes. 13. Indian Public Finance – Indian Revenue, Foreign Aid. 14. Indian Banking and Currency system.
C. MATHEMATICS
Algebra: Algebra of sets, relations and functions, Inverse of a function, equivalence relation.The system of complex numbers, De Moivere’s Theorem and its simple applications. Relation between roots and coefficients of a polynomial equation – Evaluation of symmetric function of roots of cubic and biquadratic equation.
Algebra of Matrices: Determinants, Simple properties of determinants, Multiplication of determinants of orders two and three, Singular and non-singular matrices. Inverse of a matrix, Rank of a matrix and application of matrices to the solution of linear equations ( in three unknowns ). Convergence of sequences, and series, tests of convergence of series with positive terms, Ratio, Root and Gauss tests. Analytic Geometry: Straight lines, Circles, System of circles, parabola, ellipse and hyperbola in standard form and their elementary properties, Classification of curves second degree. Differential Equation: First order differential equation. Solution of Second and higher order linear differential equations with constant coefficients and simple applications.
Differential and Integral Calculus: Limit, continuity and differentiability of functions, successive differentiation, derivatives of standard functions, Rolle’s and Mean-value Theorems, Maclaurins and Taylor’s series ( without proof) and their applications, Maxima and Minima of functions of one and two variables. Tangents and Normals, Curvature, Partial differentiation, Euler’s theorem for homogeneous function, Tracing of curves. Standard methods of integration, Riemann’s definition of definite integral, fundamental theorem of integral calculus, quadrature, rectification, volumes and surface area of solids of revolution. Statistics: Frequency distributions, Measures of central tendency, measures of dispersion, Skewness and Kurtosis, Random variables and distribution function, Discrete distributions, Binomial and Poisson distribution, continuous distributions, Rectangular, Normal and Exponential distributions, Principles of least squares, correlation and regression, Random Sampling, random numbers, Sampling of attributes, Large Sample tests for mean and proportion, Tests of significance based on t, F and Chi-square distributions.
D. COMMERCE
This paper will cover all the subjects of commerce ordinarily taught at the B.Com. or similar degree courses of Indian Universities. Specifically, it will include the following subjects: Accountancy: Conceptual framework, Income measurement, Final accounts, Accounting for partnership firms, Hire-purchase accounting, Corporate accounting ( Issue, forfeiture and re-issue of shares ). Business Organisation: Business objectives, Business environment, Business entrepreneurship ( including location, choice of form of business and growth strategies ), Business operations including finance, production, marketing and human resource development. Management: Concept of management, Planning, Organising, Leading and Controlling. Micro-economics: Price-mechanism, Theory of consumer behaviour, Elasticity of demand, Production function, Theory of costs, Market structures, Price-determination under perfect competition and monopoly.
Indian Economics: Issues involved in planning for economic development, Sectoral analysis of Indian economy including agriculture, industry and foreign trade. Business Statistics: Analysis of Univariate data involving measurement of Central tendency and dispersion, correlation and regression analysis, index numbers, analysis of time-series, Theory of probability. Business Law: Indian Contract Act, 1872, Sale of Goods Act, 1930, Partnership Act, 1932 and Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881.
Company Law: Kinds of companies, matters involving incorporation of company, shares and share capital and matters relating to issue and transfers of shares, members of a company, management of a company, meetings and resolutions, winding up of a company. Cost accounting: Procedures involved in cost accounting, marginal costing, cost-volume profit analysis, Budgetary control, Standard costing. Auditing: Meaning and objects of auditing, Types of audit, Audit process. Income Tax: Basic concepts, Residence and tax liability, heads of income. .