HOW TO KICK-START UPSC PREPARATION
Introduction
UPSC conducts recruitment for the Top level Central government services via the Civil Service Examination. The Group A and Group B services part of this examination are:
Interview of Swapnil Patil - IAS 2017 ,AIR 55 (Topper - Mumbai region)
Q.Introduction
Ans.
- Name: Swapnil Patil
- Residence: Kurla, Mumbai
- Education: 10th (88.53%) , 12th (84.5%) and B.E (Ex&TC) = 60%.
- Attempt: Fourth
- Cadre: Maharashtra
Q.UPSC IAS 2017 scorecard
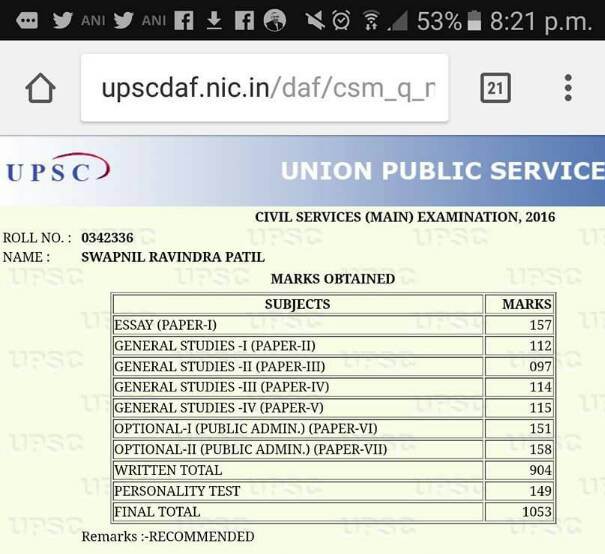
Ans.Prelims score is approx 130.
Q.UPSC IAS 2017 prepraration booklist
Ans.
- History – Must Read NCERT Books
- —6th – Our Pasts 1
- —7th – Our Pasts II
- —8th – Our Pasts III – Part 1, Part 2
- —9th – India & the Contemporary World 1
- —10th – India & the Contemporary World II
- —11th – Themes in World History (Focus on –Industrial Revolution)
- —12th – Themes in Indian History I, Themes in Indian History II, Themes in Indian History III
- Modern Spectrum RAJIV AHIR for prelims, GROVER
- MAINS : BIPAN CHANDRA Part 1 and Part 2 ....India before Gandhi and India After Gandhi by Ramchandra Guha could be done.
- Geography – Must Read NCERT Books
- —6th – The Earth : Our Habitat
- —7th – Our Environment
- —8th – Resources & Development
- —9th – Contemporary India 1
- —10th – Contemporary India II
- —11th – Fundamentals of Physical Geography, —11th – India – Physical Environment
- —12th – Fundamentals of Human Geography, —12th – India – People & Economy for prelims Geography ...one can do GC Leong ISC certified Physical geography ...and a good ATLAS of Penguin publications should be referred
- for Mains NCERT will be suffice.
- Economics – Must Read NCERT Books
- —9th – Economics
- —10th – Understanding Economic Development
- —11th – Indian Economic Development
- —12th – Introductory Microeconomics
- —12th – Introductory Macroeconomics, —Class XII – Supplementary reading material in Economics – Introductory Macroeconomics
- Economics prelim i recommend SRIRAM IAS notes along with Ramesh Singh of Tata Mcgraw Hill publications
- Eco Mains ..having hold on newspaper is very important ...i would recommending following Economic Times or Business Standard or Mint (selective reading)
- Political Science – Must Read NCERT Books
- —9th – Democratic Politics I
- —10th – Democratic Politics II
- —11th – Indian Constitution at Work
- —11th – Political Theory
- —12th – Contemporary World Politics (–8th – Environment & Natural Resources)
- —12th – Politics in India Since Independence
- Polity ...Laxmikant is the Bible ...need to done byheart ...20 readings minimum for Prelims
- Mains i would recommend visiting prsindia.org for continuos tracking of all kinds of legislations proposed,drafted and passed in Parliament along with reports of various Committee reports .....
- Along with this reading newspaper editorials relating to Consitution, Judicial court judgements, etc need to be studied
- Sociology – Must Read NCERT Books
- —12th – Social Change & Development in India for GS MAINS following books are recommended
- Indian Society – Ram Ahuja
- Social Problems in India – Ram Ahuja
- Culture/Fine Arts – Must Read NCERT Books
- —11th – An Introduction to Indian Art for culture i would recommend referring to CCRT website, NIOS culture notes are good and current culture events should also tracked selectively
- Science – Must Read NCERT Books For science, aspirants are advised to go through at-least these selected chapters from the mentioned standards.
- —6th – ◦9: The Living Organisms & their Surroundings
- —7th – ◦7: Weather, Climate & Adaptations of Animals, ◦9: Soil
- —8th – ◦1: Crop Production & Management, ◦5: Coal & Petroleum, ◦7: Conservation of Plants & Animals, ◦12: Friction, ◦18: Pollution of Air & Water
- —9th – ◦14: Natural Resources
- —10th – ◦14: Sources of Energy, ◦15: Our Environment, ◦16: Management of Natural Resources
- —12th (Biology) – ◦Unit X: Ecology (13 – Organisms & Population, 14 – Ecosystem, 15 – Biodiversity & Conservation, 16 – Environmental Issues)
- Mains , emphasis must be given on current science events lke achievements of ISRO , inventions by BARC,DRDO and various Indian institutes...apart from this 'major' international inventions and discoveries must also be tracked
- ETHICS
- for ethics one may begin with LEXICON , emphasis has to be given on thinkers foreign and Indian thinkers .....their teachings must be reflected in the answers and case studies to earn more marks !
- Current Affairs
- Yojana
- Kurukshetra
- DowntoEarth
- Science Reporter etc.
Q.Which is preferable books or electronic media
Ans.UPSC demands up to date knowledge and so every topic must be covered from 360° so books can give us a good start but internet is indispensable.
Q.Which is graduation can give advantage to a candidate
Ans.Any graduation can be chosen based on the candidates choice but Arts is preferable if his aim is to go for UPSC. As a backup he can choose UGC NET/SET and join as a professor
Q.What was your schedule
Ans.
- Wakeup: 7 am
- Start studying: 9 am to 1pm
- Lunch: 1-1:30
- Studying: 1:30-5:00pm
- Sports: 5:00 - 5:30 pm
- Studying: 5:30 - 10:00pm
- Sleep: 11:00pm - 7:00am
This was for 6 days a week.
Q.How did you divide between mains and prelims preparation
Ans. I continued both till March and after March focused on only prelims till prelims got over.
Q.Are coaching classes necessary
Ans. Coaching institutes can show you the road but only self study can help you cross the finish line.
Q.Any points to remember during interview and medical tests
Ans. For the interview read the DAF very carefully and go through schemes and important projects of your home state as these are very important. The panel usually asks situation based questions a lot. And if you have to criticise the government then take a balanced approach. For the medical tests go on an empty stomach, no permanent tattoos are allowed and make sure your vision is good as color blindness might make you ineligible for IPS.
How to use upscfever.com for preparation
Every year the UPSC CSE prelims is held in August. The exam is the most competitive exam of India. Nearly 11 lakh candidates register for it but less than half actually appear. Around 1 lakh serious candidates are there and out of these 15000 - 16000 are selected for the mains examination. Vacancies are around 1300. To be assured of being selected a candidate has to score around 120+ in prelims Paper I and qualify paper II.
Preparation for the examination must cover current affairs of past three years and host of other topics. A candidate must have the habit of reading relevant articles of newspapers like Times of India, Indian express.
The list of subjects needed for prelim Paper I are given below. Ideally a candidate must begin with history and polity. Both are easiest subjects of the lot. Science is usually more about current affairs and less from textbooks but as it has the smallest syllabus it should be next. Economy from textbooks as well as Economic survey is enough for the exam as questions are very easy.
The toughest part is MCQ's of geography, environment and culture. Regarding environment, current affairs of international treaties as well as very tough questions can be asked. Culture is tough to predict and so thorough coverage not possible but certain basic topics can be covered which overlap with History.
- Start History , polity around August.
- Science and economy by mid September.
- Geography and environment by November. Keep an eye out for government schemes and International summits like SAARC, BRICS etc.
- Economic survey is released with the budget in February and India yearbook in January. They have to be read.
- Culture by March.
UPSC CSE has the following subjects for preparation:
| Subject |
Click below |
| General Aptitude | link |
| History | link |
| Geography | link |
| Environment | link |
| Science | link |
| Polity | link |
| Culture | link |
| Current affairs | India Yearbook and Economic survey |
| Economy | link |
| Aptitude | link |
Mains examination:
Preparation for mains can start after prelims is over without waiting for the result. Optional subject like Public administration has two papers. first one needs reading textbooks but second paper is 80% on current affairs.
| Subject |
Click me |
| Ethics | link |
| Public administration | link |
Don't be dejected if you fail to clear prelims. Start the cycle again. Remember UPSC CSE is a marathon not a sprint, you have to keep running.
Services
Group A Services
- Indian Administrative Service
- Indian Audit and Accounts Service
- Indian Civil Accounts Service
- Indian Corporate Law Service
- Indian Defence Accounts Service
- Indian Defence Estates Service
- Indian Foreign Service
- Indian Information Service
- Indian Ordnance Factories Service
- Indian Police Service
- Indian Post & Telecommunication Accounts and Finance Service
- Indian Postal Service
- Indian Railway Accounts Service
- Indian Railway Personnel Service
- Indian Railway Traffic Service
- Indian Revenue Service (Income Tax)
- Indian Revenue Service (CBEC)
- Indian Trade Service
- Railway Protection Force
Group B Services
- Armed Forces Headquarters Civil Service
- Delhi, Andaman and Nicobar Islands Civil Service
- Delhi, Andaman and Nicobar Islands Police Service
- Pondicherry Civil Service
- Pondicherry Police Service
The coveted amongst these services are the Indian Administrative Service (I.A.S) , Indian Police Service (I.P.S) and the Indian Foreign Service (I.F.S).
Examination
The examination has three parts:- Civil Service Aptitude Test: It has two 200 marks objective type tests. 1/3 rd negative marks for wrong answers. Paper - I is General Studies and Paper - II is General Ability test. Since CSAT-2015 the Paper - II has become qualifying only with 33% marks required to clear it. Paper - I shall decide the eligibility for the next round. Marks aren't counted in the final merit list. Paper - I has 100 MCQ's and Paper - II has 80.
- Current events of national and international importance
- History of India and Indian National Movement.
- Indian and World Geography - Physical, Social, Economic Geography of India and the World.
- Indian Polity and Governance - Constitution, Political System, Panchayati Raj, Public Policy, Rights Issues, etc.
- Economic and Social Development - Sustainable Development, Poverty, Inclusion, Demographics, Social Sector initiatives, etc.
- General issues on Environmental Ecology, Bio-diversity and Climate Change - that do not require subject specialization
- General Science
Duration: Two hours
- Comprehension Interpersonal skills including communication skills;
- Logical reasoning and analytical ability
- Decision-making and problem solving
- General mental ability Basic numeracy (numbers and their relations, orders of magnitude, etc.) (Class X level), Data interpretation (charts, graphs, tables, data sufficiency etc. - Class X level)
Note 1 : Paper-II of the Civil Services (Preliminary) Examination will be a qualifying paper with minimum qualifying marks fixed at 33%
Note 2 : The questions will be of multiple choice, objective type.
Note 3: It is mandatory for the candidate to appear in both the Papers of Civil Services (Prelim) Examination for the purpose of evaluation.
QUALIFYING PAPERS ON INDIAN LANGUAGES AND ENGLISH
The aim of the paper is to test the candidates ability to read and understand serious discursive prose, and express his ideas clearly and correctly, in English and Indian Language concerned. The pattern of questions would be broadly as follows :- (i) Comprehension of given passages (ii) Precis Writing (iii) Usage and Vocabulary (iv) Short Essays Indian Languages :- (i) Comprehension of given passages (ii) Precis Writing (iii) Usage and Vocabulary (iv) Short Essays (v) Translation from English to the Indian language and vice-versa.
PAPER-I Essay: Candidates may be required to write essays on multiple topics. They will be expected to keep closely to the subject of the essay to arrange their ideas in orderly fashion and to write concisely. Credit will be given for effective and exact expression
PAPER-II General Studies- I:
Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of the World and Society. Indian culture will cover the salient aspects of Art Forms, Literature and Architecture from ancient to modern times. Modern Indian history from about the middle of the eighteenth century until the present- significant events, personalities, issues The Freedom Struggle - its various stages and important contributors /contributions from different parts of the country. Post-independence consolidation and reorganization within the country,History of the world will include events from 18th century such as industrial revolution, world wars, redrawal of national boundaries, colonization, decolonization, political philosophies like communism, capitalism, socialism etc.- their forms and effect on the society. Salient features of Indian Society, Diversity of India. Role of women and women's organization, population and associated issues, poverty and developmental issues, urbanization, their problems and their remedies. Effects of globalization on Indian society Social empowerment, communalism, regionalism & secularism. Salient features of world's physical geography. Distribution of key natural resources across the world (including South Asia and the Indian sub-continent); factors responsible for the location of primary, secondary, and tertiary sector industries in various parts of the world (including India) Important Geophysical phenomena such as earthquakes, Tsunami, Volcanic activity, cyclone etc., geographical features and their location- changes in critical geographical features (including water-bodies and ice-caps) and in flora and fauna and the effects of such changes.
PAPER-III General Studies- II: Governance, Constitution, Polity, Social Justice and International relations.
Indian Constitution- historical underpinnings, evolution, features, amendments, significant provisions and basic structure. Functions and responsibilities of the Union and the States, issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure, devolution of powers and finances up to local levels and challenges therein. Separation of powers between various organs dispute redressal mechanisms and institutions. Comparison of the Indian constitutional scheme with that of other countries Parliament and State Legislatures - structure, functioning, conduct of business, powers & privileges and issues arising out of these. Structure, organization and functioning of the Executive and the Judiciary Ministries and Departments of the Government; pressure groups and formal/informal associations and their role in the Polity. Salient features of the Representation of People's Act. Appointment to various Constitutional posts, powers, functions and responsibilities of various Constitutional Bodies. Statutory, regulatory and various quasi-judicial bodies Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.Development processes and the development industry- the role of NGOs, SHGs, various groups and associations, donors, charities, institutional and other stakeholders Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes; mechanisms, laws, institutions and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of these vulnerable sections. Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources. Issues relating to poverty and hunger. Important aspects of governance, transparency and accountability, e-governance- applications, models, successes, limitations, and potential; citizens charters, transparency & accountability and institutional and other measures. Role of civil services in a democracy. India and its neighborhood- relations. Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India's interests Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India's interests, Indian diaspora. Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
PAPER-IV General Studies-III: Technology, Economic Development, Bio diversity, Environment, Security and Disaster Management.
Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment. Inclusive growth and issues arising from it. Government Budgeting. Major crops cropping patterns in various parts of the country, different types of irrigation and irrigation systems storage, transport and marketing of agricultural produce and issues and related constraints; e-technology in the aid of farmers Issues related to direct and indirect farm subsidies and minimum support prices; Public Distribution System- objectives, functioning, limitations, revamping; issues of buffer stocks and food security; Technology missions; economics of animal-rearing. Food processing and related industries in India- scope and significance, location, upstream and downstream requirements, supply chain management. Land reforms in India. Effects of liberalization on the economy, changes in industrial policy and their effects on industrial growth. Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc. Investment models. Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life Achievements of Indians in science & technology; indigenization of technology and developing new technology. Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, robotics, nano-technology, bio-technology and issues relating to intellectual property rights. Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment Disaster and disaster management. Linkages between development and spread of extremism. Role of external state and nonstate actors in creating challenges to internal security. Challenges to internal security through communication networks, role of media and social networking sites in internal security challenges, basics of cyber security; money-laundering and its prevention Security challenges and their management in border areas;linkages of organized crime with terrorism Various Security forces and agencies and their mandate
PAPER-V General Studies- IV: Ethics, Integrity, and Aptitude
Ethics and Human Interface: Essence, determinants and consequences of Ethics in human actions; dimensions of ethics; ethics in private and public relationships. Human Values - lessons from the lives and teachings of great leaders, reformers and administrators; role of family, society and educational institutions in inculcating values. Attitude: content, structure, function; its influence and relation with thought and behaviour; moral and political attitudes; social influence and persuasion. Aptitude and foundational values for Civil Service , integrity, impartiality and non-partisanship, objectivity, dedication to public service, empathy, tolerance and compassion towards the weaker-sections. Emotional intelligence-concepts, and their utilities and application in administration and governance.Contributions of moral thinkers and philosophers from India and world. Public/Civil service values and Ethics in Public administration: Status and problems; ethical concerns and dilemmas in government and private institutions; laws, rules, regulations and conscience as sources of ethical guidance; accountability and ethical governance; strengthening of ethical and moral values in governance; ethical issues in international relations and funding; corporate governance. Probity in Governance: Concept of public service; Philosophical basis of governance and probity; Information sharing and transparency in government, Right to Information, Codes of Ethics, Codes of Conduct, Citizen's Charters, Work culture, Quality of service delivery, Utilization of public funds, challenges of corruption. Case Studies on above issues.
OPTIONAL PAPERS
PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION PAPER – I
Administrative Theory 1. Introduction: Meaning, scope and significance of Public Administration; Wilson’s vision of Public Administration; Evolution of the discipline and its present status; New Public Administration; Public Choice approach; Challenges of liberalization, Privatisation, Globalisation; Good Governance: concept and application; New Public Management. 2. Administrative Thought: Scientific Management and Scientific Management movement; Classical Theory; Weber’s bureaucratic model – its critique and post-Weberian Developments; Dynamic Administration (Mary Parker Follett); Human Relations School (Elton Mayo and others); Functions of the Executive (C.I. Barnard); Simon’s decision-making theory; Participative Management (R. Likert, C. Argyris, D. McGregor). 3. Administrative Behaviour: Process and techniques of decision-making; Communication; Morale; Motivation Theories – content, process and contemporary; Theories of Leadership: Traditional and Modern. 4. Organisations: Theories – systems, contingency; Structure and forms: Ministries and Departments, Corporations, Companies, Boards and Commissions; Ad hoc and advisory bodies; Headquarters and Field relationships; Regulatory Authorities; Public - Private Partnerships. 5. Accountability and control: Concepts of accountability and control; Legislative, Executive and Judicial control over administration; Citizen and Administration; Role of media, interest groups, voluntary organizations; Civil society; Citizen’s Charters; Right to Information; Social audit. 6. Administrative Law: Meaning, scope and significance; Dicey on Administrative law; Delegated legislation; Administrative Tribunals. 7. Comparative Public Administration: Historical and sociological factors affecting administrative systems; Administration and politics in different countries; Current status of Comparative Public Administration; Ecology and administration; Riggsian models and their critique. 8. Development Dynamics: Concept of development; Changing profile of development administration; ‘Antidevelopment thesis’; Bureaucracy and development; Strong state versus the market debate; Impact of liberalisation on administration in developing countries; Women and development - the self-help group movement. 9. Personnel Administration: Importance of human resource development; Recruitment, training, career advancement, position classification, discipline, performance appraisal, promotion, pay and service conditions; employer-employee relations, grievance redressal mechanism; Code of conduct; Administrative ethics. 10. Public Policy: Models of policy-making and their critique; Processes of conceptualisation, planning, implementation, monitoring, evaluation and review and their limitations; State theories and public policy formulation. 11. Techniques of Administrative Improvement: Organisation and methods, Work study and work management; e-governance and information technology; Management aid tools like network analysis, MIS, PERT, CPM. 12. Financial Administration: Monetary and fiscal policies; Public borrowings and public debt Budgets - types and forms; Budgetary process; Financial accountability; Accounts and audit.
PAPER - II Indian Administration
1. Evolution of Indian Administration: Kautilya’s Arthashastra; Mughal administration; Legacy of British rule in politics and administration - Indianization of public services, revenue administration, district administration, local self-government. 2. Philosophical and Constitutional framework of government: Salient features and value premises; Constitutionalism; Political culture; Bureaucracy and democracy; Bureaucracy and development. 3. Public Sector Undertakings: Public sector in modern India; Forms of Public Sector Undertakings; Problems of autonomy, accountability and control; Impact of liberalization and privatization. 4. Union Government and Administration: Executive, Parliament, Judiciary - structure, functions, work processes; Recent trends; Intragovernmental relations; Cabinet Secretariat; Prime Minister’s Office; Central Secretariat; Ministries and Departments; Boards; Commissions; Attached offices; Field organizations. 5. Plans and Priorities: Machinery of planning; Role, composition and functions of the Planning Commission and the National Development Council; ‘Indicative’ planning; Process of plan formulation at Union and State levels; Constitutional Amendments (1992) and decentralized planning for economic development and social justice. 6. State Government and Administration: Union-State administrative, legislative and financial relations; Role of the Finance Commission; Governor; Chief Minister;Council of Ministers; Chief Secretary; State Secretariat; Directorates. 7. District Administration since Independence: Changing role of the Collector; Unionstate-local relations; Imperatives of development management and law and order administration; District administration and democratic decentralization. 8. Civil Services: Constitutional position; Structure, recruitment, training and capacity-building; Good governance initiatives; Code of conduct and discipline; Staff associations; Political rights; Grievance redressal mechanism; Civil service neutrality; Civil service activism. 9. Financial Management: Budget as a political instrument; Parliamentary control of public expenditure; Role of finance ministry in monetary and fiscal area; Accounting techniques; Audit; Role of Controller General of Accounts and Comptroller and Auditor General of India. 10. Administrative Reforms since Independence: Major concerns; Important Committees and Commissions; Reforms in financial management and human resource development; Problems of implementation. 11. Rural Development: Institutions and agencies since independence; Rural development programmes: foci and strategies; Decentralization and Panchayati Raj; 73rd Constitutional amendment. 12. Urban Local Government: Municipal governance: main features, structures, finance and problem areas; 74th Constitutional Amendment; Globallocal debate; New localism; Development dynamics, politics and administration with special reference to city management. 13. Law and Order Administration: British legacy; National Police Commission; Investigative agencies; Role of central and state agencies including paramilitary forces in maintenance of law and order and countering insurgency and terrorism; Criminalisation of politics and administration; Police-public relations; Reforms in Police. 14. Significant issues in Indian Administration: Values in public service; Regulatory Commissions; National Human Rights Commission; Problems of administration in coalition regimes; Citizen-administration interface; Corruption and administration; Disaster management
- Interview: 275 marks for the interview. Candidates selected after mains qualify for the interview.