-
Chapter 10: ORGANIZATION
Introduction
Administration is a cooperative effort of a group of people in pursuit of a common objective. Organization is an important element of an organization. It facilitates proper use of that group and resources.
- It is the form of every human association for attainment of a common purpose.
- The relating of efforts and capacities of individuals and groups upon a task in such a way as to secure the objective with least friction and most satisfaction for whom the task is done and those engaged in the enterprise.
- Organization is both a structure and a set of human relationships.
- Other features are: Division of labor, power, responsibility, presence of multiple power centers, substitution of personnel.
Gulick's Theory: Four Basis of Organizations
I: Persons: Group of people served by the organization.
Advantage: Makes one agency responsible for all needs of a group. Facilitates coordination of different services provided for the beneficiaries. Establishes close relationship between target group and agency. Enables wholistic approach to problems.
Disadvantage: Creation of niche departments. Jurisdictional disputes.Violates the principle of specialization due to multi-functional character. Makes organization vulnerable to improper influence of pressure groups. This Principle doesn't have universal application.
II: Purpose: Functions performed by the organization. Identify functions and goals and create a department for each.
Advantages: Coherent mission of organizations. Eliminates overlapping and duplication of work. Facilitates development of coordinated policies. Fixation of responsibility for failures. Easily intelligible to common man. Self containment of organization and low coordination costs. Work under a single director who exercises control over all personnel.
Disadvantage: Neglects subordinate type of work. Ignores latest technologies. Leads to departmentalization in thinking.
III Process: Specialized skill used by organization in performance of work since it involves use of same knowledge, skills and processes.
Advantages: Maximizes specialization, utilization of technical skill,. Secures economy due to mas utilization of labor saving machinery. Encourages coordination in technology. Work is conducive to development of career service.
Disadvantage: Neglect of generalists. Focus on means than ends. Professional conflicts. Cannot apply to non technical activities.
IV Place: Territorial area covered by the organization.
Advantage: Intensive development of an area. Facilitates coordination of different services provided in a single area. Allows adaptation of national policies to area. Suitable in cases of long distance and communication difficulties. It secures economy due to reduction in travel and communication cost.
Disadvantage: Counter to uniformity in administration of national policies. Fosters localism at cost of national outlook. Violates principles of specialization due to multi-functional nature. Can come under influence of regional interests, pressure groups.
Cons of Gulick's theory:
- Gulick didn't consider culture in which an organization is located or its environment or personnel and political factors. The theory is criticized as vague, incompatible with each other, focus on prescriptive approach i.e. how work should be divided not descriptive i.e. how it is divided.
- Some organizations might have all four types of departments due to situational factors, efficiency requirements and goals.
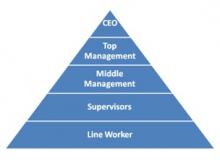
Hierarchy [ A scalar process or Chain ]
It is a grading of duties not according to different functions but as per the degree of authority and corresponding responsibility. It is a chain of command - an unbroken line of authority that extends from top of organization to bottom and clarifies who reports to whom.
Principles of hierarchy
- Principles of proper channel: All command and communication should pass through proper channel. No intermediate level can be skipped in business.
- Principles of correspondence: Authority and responsibility should be coequal and coterminus at all levels.
- Principle of Unity of Command: Subordinates should receive orders from single superior only.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Integration, coherence | red tapism |
| used as a channel of communication | discourages initiative and drive of lower personnel. |
| fix responsibility at each level and no short circuiting. | Top loses touch with lower levels. Not conducive for growth of dynamic human relations. |
| Prevents congestion at top. | Creates superior subordinate differences at various levels w.r.t pay, qualifications, responsibilities, distribution of authority. |
| Decentralization, delegation of duties | |
| simple procedure for file management | |
| discipline, coordination and order. |
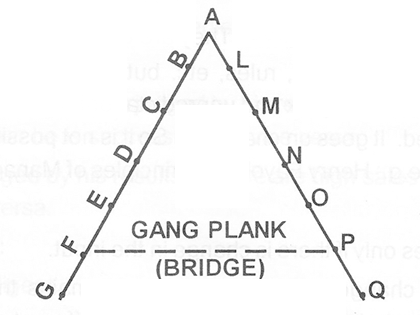
Fayol's Gang plank
To speed flow of business and avoid delay in disposal of cases. Allow direct communication between people at same level but in different departments after clearance of immediate superiors.