-
Chapter 21: ADMINISTRATIVE BEHAVIOR
Introduction to Decision Making
Herbert Simon proposed this theory where decision making is an act of determining in one's own mind upon an opinion or course of action. Involves a conscious choice of one behavior alternative from a group of two or more alternatives. A decision is made within the guidelines established by a policy. A policy is relatively extensive, affects many problems and is used again and again. A decision applies to a particular problem and has a non continuous type of usage.
As per Simon, it is important to study the operative staff and supervisory staff. The supervisors should be capable of influencing operative staff towards coordinated, effective behavior. Insight into structure and function of the organization can best be gained by analyzing the manner in which the decision and behavior of employees are influenced within and by the organization.
Organization modes to influence decision making:
- Authority: Subordinate follows orders of superiors without latter having to convince him.
- Organizational loyalties: Each member identifies himself as part of an organization and takes decision for organization's interest.
- Criteria for efficiency: Efficiency is the criteria that influences decisions of members.
- Advice and information should be available to individuals to make judgments.
- Training prepares members to take satisfactory decisions.
Classical thinkers didn't view decision making as an important activity related to management functions like planning, organizing, coordinating so on. They were concerned with decision making only to the extent that it affects delegation and authority. Taylor referred to scientific method as the only ideal approach to making decisions.
Simon said decision making is an all embracing activity that encompasses all administrative functions like "POSDCORB" or "POCCC". He was against the classical idea of universal principles of administration.
Simon's basis of Decision Making:
- Every decision has two bases - Factual i.e. proved by observations, measurable means and Values i.e. subjectively asserted as valid.
- Value deals with selection of final goals and is used at higher levels and Fact deals with implementation of goals and is needed at lower levels.
Intelligence activity: It involves finding occasions for making a decision. People survey ecology, technology, political and social environment to identify new conditions that call for new actions.
Decision Activity: Here people spend an even larger time in inventing, developing, designing possible courses of action for handling situations where a decision is needed.
Choice activity: Choosing a course of action from given alternatives which are already developed, analysed for their consequences to meet a problem.
Each phase is itself a complex decision making process. In design phase again new intelligence phase may be needed. The problem may have sub problems each with Intelligence, Decision and choice activity.
Simon believes that a manager doing both routine and long term planning devotes more time to routine activities. Thus routine drives out non programmed activity.
| Types of decision | Traditional technique | Modern technique |
| Programmed i.e. routine, repetitive, organization develops specific process for handling them | Habit, clerical routine method | operation research, analysis models, computer simulations, electronic data processing |
| Non programmed i.e. one shot, ill structured, novel, policy decisions handled by general problem solving process | judgment, intuition, creativity, rule of thumb | heuristic problem solving applied to training human decision makers, constructing heuristic computer programs |
Simon's Bounded Rationality Model of Decision Making
Simon viewed rationality as "Selection of preferred behavior alternatives in terms of value whereby the consequences of behavior can be evaluated".
Component of a decision:
- Objectively rational: Maximize given values in a given situation
- Subjectively rational: Maximize attainment relative to a actual knowledge of subject
- Consciously rational: Adjustment of means to ends is a conscious process.
- Deliberately rational: Adjustment of means to ends is deliberately brought about.
- Organizationally rational: Its oriented to organizations goals.
- Personally rational: Oriented to individuals goals.
Total rationality is impossible hence we can't have 'maximizing decisions'. Human behavior in an organization is characterized by 'bounded rationality' leading to 'satisfying decisions'.
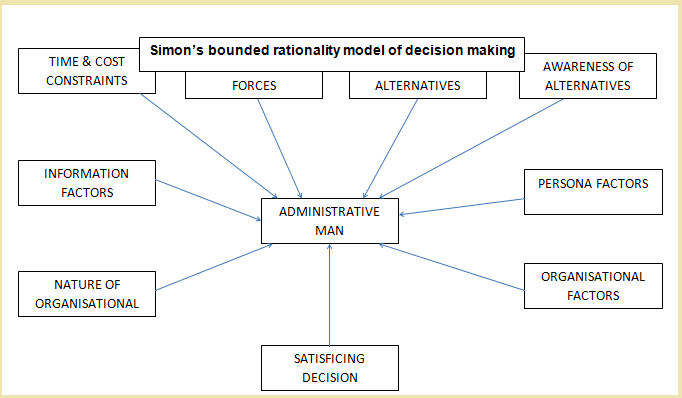
In view of the limitations Simon proposes the administrative man against the model of economic man who takes maximizing decisions.
- Administrative man chooses between alternatives and selects one that is good enough.
- Recognizes the world he perceives is simplified model of the real world.
- Can make a decision using Rule of Thumb as he treat world as empty.
- Can make decisions by considering the alternatives are all possible cases as he only satisfies.
Critics to Simon's theory have claimed that fact, value distinction is in a new way revising the politic administrative dichotomy and considers bureaucracy as a neutral instrument. C. Argyris observes that Simon hasn't considered role of intuition, tradition, faith in decision making. He said Simon's theory uses 'satisfying decisions' to rationalize incompetence.