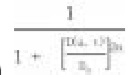
UGCNET Computer Science December 2014 Paper III
View Answer
Ans .
(A) 157.5 n.sec.
Explanation : The average access time of the system for memory read cycle is 0.8x50+0.2x350=110ns.
View Answer
Ans .
(C) Software interrupts
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(A) 125 chars/second and 0.8 seconds
Explanation : Time to print a character = 6+2=8 m.sec.
View Answer
Ans .
(D) ii iv i iii
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) 07
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(D) 00, 0, 1, 1
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(A) I, II and III
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(D) II and III
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) Check-pointing
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) ABCD, E
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(D) None of the statements are correct.
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(A) Every binary relation is never be in BCNF.
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(D) None of the above
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(C) i ii iii iv
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) Dithering
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(A) A'(-1,√2 - 1), B'(-1,2√2 - 1), C'(3/2√2 – 1, 9/2√2 – 1)
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B)
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(D) i ii iii iv
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(C) S2 and S1 are true.
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(A) 12
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(C) MPI_Send and MPI_Recv are non-blocking message passing routines of MPI.
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) L = {an bn | n ≥ 0}
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(D) L1 is not regular and L2 is not regular.
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(D) None of the above
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(D) n(n – 1)/2
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) 320
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) Fragment offset
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
Marks given to all
Explanation : 48000km/(2.4*108)= 48*106m/(2.4*108)= 20×10-2 =200×10-3s.=200ms
View Answer
Ans .
(B) HDLC
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(A) Private key is kept by the receiver and public key is announced to the public.
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(C) (nlgn)
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(C) iv ii iii i
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(D) None of the above
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(C) Greedy algorithm, Dynamic programming algorithm
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) 10
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(C) 927, 204,913, 242, 914, 247, 365
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) Synchronized methods
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(A)
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(D) Autoboxing
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(D) All of the above
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(A) Stereotype is used for extending the UML language.
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(C) init( )
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) Function point metric
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) 14
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) $ 20,160
Explanation : Total resusable components planned=60.
View Answer
Ans .
(C) 1
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(A) Count of the number of components that can call, or pass control, to a component A
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(D) Cohesion with respect to time
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(D) Magnetic tapes optical disks magnetic disks electronic disks main memory cache registers
Explanation :
View Answer
ok
Ans .
Marks given to all
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(D) 61
Explanation : 11->12->9->16->1->34->36.=1+3+7+15+33+2=61
View Answer
Ans .
(A) P2 P1 P3
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(A) It is higher level synchronization primitive and is a collection of procedures,variables, and data structures grouped together in a special package.
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) Logical combination of physical memories on the nodes.
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(C) x (~F[x])
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) generates all successor nodes and computes an estimate of distance (cost) from start node to a goal node through each of the successors. It then chooses the successor with shortest cost.
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(3) Identical with average revenue
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) iv iii ii i
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) iv iii i ii
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) III and IV
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(D) LDCF LCF LCS LREC LRE
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) ii iv i iii
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) with | vxy | m, and | vy | 1, such that uvi xyi z L for all i = 0, 1, 2, …….
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) only S2
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(D) a =1/4, b =1/4, c =1/4, d =1/4
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(A)
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) Infeasible
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(C) the solution so obtained is not feasible
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(C) 13
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(D) I is true and II is true
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(3) Identical with average revenue
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(A) i ii iii iv
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(A) Windows Vista
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(A) A program that performs a legitimate function that is known to an operating system or its user and also has a hidden component that can be used for nefarious purposes like attacks on message security or impersonation.
Explanation :
View Answer
Ans .
(B) Parallel computing
Explanation :
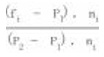
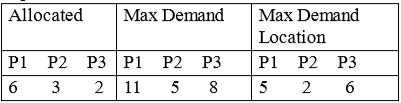 Total tapes 13. Allocated 11. Balance 2.
Total tapes 13. Allocated 11. Balance 2.