UGCNET Computer Science December 2015 Paper II
Ans .
(B) 52492
- Explanation :
We must choose at least 3 women, so we calculate the case of 3 women, 4 women and 5 women and by addition rule add the results.
12C3 x 20C2 + 12C4 x 20C1 + 12C5 x 20C0 = (12x11x10/3x2x1) x (20x19/2x1) + (12x11x10x9/4x3x2x1) x 0 + (12x11x10x9x8/5x4x3x2x1) x 1 = 220 x 190 + 495 x 20 + 792 = 52492
Ans .
(D) (d) only
- Explanation :
Euler Circuits
Hamilton Circuit
Bipartite Graph From the above definitions, we can see that (d) is false. So Answer is (D)
Ans .
(D) (d) only
- Explanation :
Ans .
(C) (v1, v4, v6, v7); (v2, v3, v5, v8)
- Explanation :
A simple graph G=(V ,E) is called bipartite if its vertex set can be partitioned into two disjoint subsets V=V1∪ V2, such that every edge has the form e=(a,b) where aϵV1 and bϵV2.
Bipartite graphs are equivalent to two-colorable graphs. 1. Assign Red color to the source vertex (putting into set V1).
2. Color all the neighbours with Black color (putting into set V2).
3. Color all neighbour’s neighbour with Red color (putting into set V1).
4. This way, assign color to all vertices such that it satisfies all the constraints of m way coloring problem where m = 2.
5. While assigning colors, if we find a neighbour which is colored with same color as current vertex, then the graph cannot be colored with 2 colors (ie., graph is not Bipartite).
So Answer is option (C).
Ans .
(D) (a), (b) and (c)
- Explanation :
Caterpillar tree: In graph theory, a caterpillar is a tree in which all the vertices are within distance 1 of a central path.
Theorem: All caterpillars are graceful.
So, (a), (b) and (c) are graceful.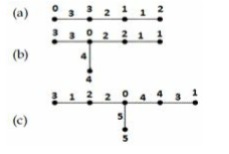
Ans .
(B) (b) and (c)
- Explanation :
(a) P: Gora gets the job
Q: Gora works hard
R: Gora gets promotion
S: Gora will be happy
The argument can bet written as
(P˄Q)→R
R→S
¬S
Therefore ¬P˅¬Q
(b) Let P: Puneet is not guilty
Q: Pankaj is telling the truth
The argument can bet written as
P˅Q
~Q
Therefore, P
Thus by disjunctive syllogism, the argument is valid.
Disjunctive Syllogism:
The disjunctive syllogism rule may be written as:
P˅Q, ¬P ⊢ Q
It may also be written as:
((P˅Q)˄¬P)→Q
where P, and Q are propositions expressed in some formal system
Ans .
(A) (a)-True; (b)-True; (c)-False
- Explanation :
Ans .
(A) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
- Explanation :
Ans .
Not matched any option
- Explanation :
because Only (a) p˅~(p˄q) is tautology.
Ans .
(D) (b) only
- Explanation :
Ans .
(B) x+x2/2!+x3/3!+x4/4!+...
- Explanation :
term =1 , sum=0
suppose inp entered = 3 so First iteration
term= 1*x/1 = x
sum = 0 + x =x
Second iteration
term = x*x/2= x2/2 =x2/2! sum= x+x2/2!
Third iteration
term = =x2/2! *x/3
=x3/3.2.1=x3/3! sum= x+x2/2!+x3/3!
and so on so sum= x+x2/2!+x3/3!+……
Ans .
(A) Both the statements (a) and (b) are correct
- Explanation :
A publicly derived class is a subtype of its base class.
Inheritance provides for code reuse. BOTH are correct
Ans .
(C) Select *from customers where city like ‘%GAR%’;
- Explanation :
For Matching Any String in Oracle Like Operator is Used. also % symbol is used as a wild card character to represent multiple characters
Ans .
(B) (ii) (iv) (i) (iii)
- Explanation :
Normalization: Reduces data redundancy in a database.
Data Dictionary: Contains metadata describing database structure.
Referential Integrity : Enforces match of primary key to foreign key.
External Schema: Define view(s) of the database for particular user(s).
Ans .
(B) Both time and space complexities are better in non-recursive than in recursive program
- Explanation :
Ans .
(B) &A[0][0][0]+w(y*z*p+z*q+r)
- Explanation :
Ans .
(A) terminate()
- Explanation :
This function is provided so that the terminate handler can be explicitly called by a program that needs to abnormally terminate, and works even if set_terminate has not been used to set a custom terminate handler
Ans .
(D) A template for a group of things with the same set of characteristics that may exist in the real world
- Explanation :
Ans .
(A) Indexes
- Explanation :
Ans .
(D) ABD
- Explanation :
ABD CLOSURE = { ABDE}={ABDEF}={ABCDEFG}
SO CANDIDATE KEY IS ABD
Ans .
(C) Error Correction
- Explanation :
IEEE 802.11 Services
Ans .
(A) Type of service
- Explanation :
Ans .
(D) 3200 bps
- Explanation :

Ans .
(A) 280
- Explanation :

Ans .
Marks to all
- Explanation :
p=3, q=13, d=7, e=3, M=5, C=?
C = Me mod n
n = p*q
= 3*13 = 39
C = 53 mod 39
= 8 Answer is 8.
Ans .
(C) 1020, 3012, 6120, 8100
- Explanation :

Ans .
(C) 45 sec
- Explanation :

Ans .
(B) 49 msec
- Explanation :
Time in msec to read a block of 1024 bytes (Access time or Disk Latency) = seek time + average rotational delay + transfer time
If there are 16384 bytes per track there are 1024/16384 tracks to be read for this block.
Seek time = 40 msec
Rotational delay = 16 msec
Transfer time = (sectors_read/sectors per rev.) x rotational delay
= (1024/16384) x 16 = 1
average rotational delay = rotational delay/2 = 16/2 = 8
access time = 40 + 8 + 1 = 49
Ans .
Marks to all
- Explanation :

Ans .
(C) gettydefs
- Explanation :
Ans .
(D) (p+1)n
- Explanation :
(a) What is the maximum number of cells possible in the base cuboid? pn. This is the maximum number of distinct tuples that you can form with p distinct values per dimensions.
(b) What is the minimum number of cells possible in the base cuboid? p. You need at least p tuples to contain p distinct values per dimension. In this case no tuple shares any value on any dimension.
(c) What is the minimum number of cells possible in the data cube, C? (2n-1)×p+1. The minimum number of cells is when each cuboid contains only p cells, except for the apex, which contains a single cell.
(d) What is the maximum number of cells possible (including both base cells and aggregate cells) in the data cube, C? (p+1)n.
The argument is similar to that of part (a), but now we have p+1 because in addition to the p distinct values of each dimension we can also choose ∗ .
Ans .
(B) 0.02%
- Explanation :
The computation is based on the simplified Bayes’ formula.
P{B|A} = (P{A|B}·P{B) / P{A}.
P{M|S} = probability that a person had meningitis, conditioned by the existence of stiff neck.
P{S|M} = probability that a person complains about stiff neck, conditioned by the existence of meningitis. = 50%=1/2
P{S} = proportion of people who complain about stiff neck. = 1/20
P{M} = proportion of people who had meningitis. = 1/50,000
Then:
P{M|S} = (P{S|M}·P{M}) / P{S} =(1/2 x 1/50,000) / 1/20 = 0.0002 = 0.02%
Ans .
(B) OLAP
- Explanation :
– OLTP (On-line Transaction Processing) is characterized by a large number of short on-line transactions (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE). The main emphasis for OLTP systems is put on very fast query processing, maintaining data integrity in multiaccess environments and an effectiveness measured by number of transactions per second. In OLTP database there is detailed and current data, and schema used to store transactional databases is the entity model (usually 3NF). – OLAP (On-line Analytical Processing) is characterized by relatively low volume of transactions. Queries are often very complex and involve aggregations. For OLAP systems a response time is an effectiveness measure. OLAP applications are widely used by Data Mining techniques. In OLAP database there is aggregated, historical data, stored in multi-dimensional schemas (usually star schema).
Ans .
(A) The Top-Down View
- Explanation :
Ans .
(C) h(k, i)=(h1(k)+ih2(k))mod m
- Explanation :
Double hashing uses the idea of applying a second hash function to the key when a collision occurs. The result of the second hash function will be the number of positions form the point of collision to insert. There are a couple of requirements for the second function: it must never evaluate to 0 must make sure that all cells can be probed
Ans .
(A) {a,b,e} {c,d,f,g,h}
- Explanation :
Check for the Cycles in the graph, you will find that node A,B,E form one cycle. node F,G form another cycle. Node C,D form another cycle. and H is having self loop.
Ans .
(D) θ(logt n)
- Explanation :
Ans .
(D) 2 4 3 13 7 6 15 17 20 18 18
- Explanation :
Use In-order Traversal i.e Left–Root–Right. following this we have first root at 15, then left sub tree root at 13, then left subtree root at 4, then left is 2 and so on which results in 2 4 3 13 7 6 15 17 20 18 18
Ans .
(C) O(1)
- Explanation :
Ans .
(A) Flow Control Policy
- Explanation :
Ans .
(A) that avoids tests at every iteration of the loop
- Explanation :
Loop unrolling is a compiler optimization applied to certain kinds of loops to reduce the frequency of branches and loop maintenance instructions. It is easily applied to sequential array processing loops where the number of iterations is known prior to execution of the loop.
The general idea of loop unrolling is to replicate the code inside a loop body a number of times. The number of copies is called the loop unrolling factor. The number of iterations is divided by the loop unrolling factor.
Ans .
(C) 01E0 h
- Explanation :
Ans .
(B) (000)* is a regular expression that matches only strings containing an odd number of zeroes, including the empty string.
- Explanation :
Ans .
(C) A software interrupt
- Explanation :
Ans .
(D) Loader
- Explanation :
Ans .
(C) Error leads to fault and fault leads to failure
- Explanation :
Ans .
(D) Glassboxing
- Explanation :
Ans .
(B) 2600
- Explanation :
We let y1=x-1, y2=y-2, y3=z-3, y4=u-0
We count the number of solutions for y1+y2+y3+y4=29-6=23
n=4, r=23
The number of solutions is C(n+r-1, r) = C(4+23-1, 23)
= C(26,23) = C(26,3) = 26x25x24/1x2x3 = 2600
Ans .
(C) 16 GB
- Explanation :
block = 2^10
block pointer size = 4B
entries possible in block = 2^10/2^2 = 256
direct pointer gives = 10 * 256 = 10 blocks
single indirect gives = 256 * 256 = 2^8 blocks
double indirect gives = 256 * 256 * 256 = 2^16 blocks
triple indirect gives = 256 * 256 * 256 * 256 = 2^24 blocks
total = 10 blocks + 2^8 blocks + 2^16 blocks + 2^24 blocks = 16843018 blocks
= 16843018 * 1024 = 17247250432 ≈ 16 GB
Ans .
(B) E-Banking
- Explanation :